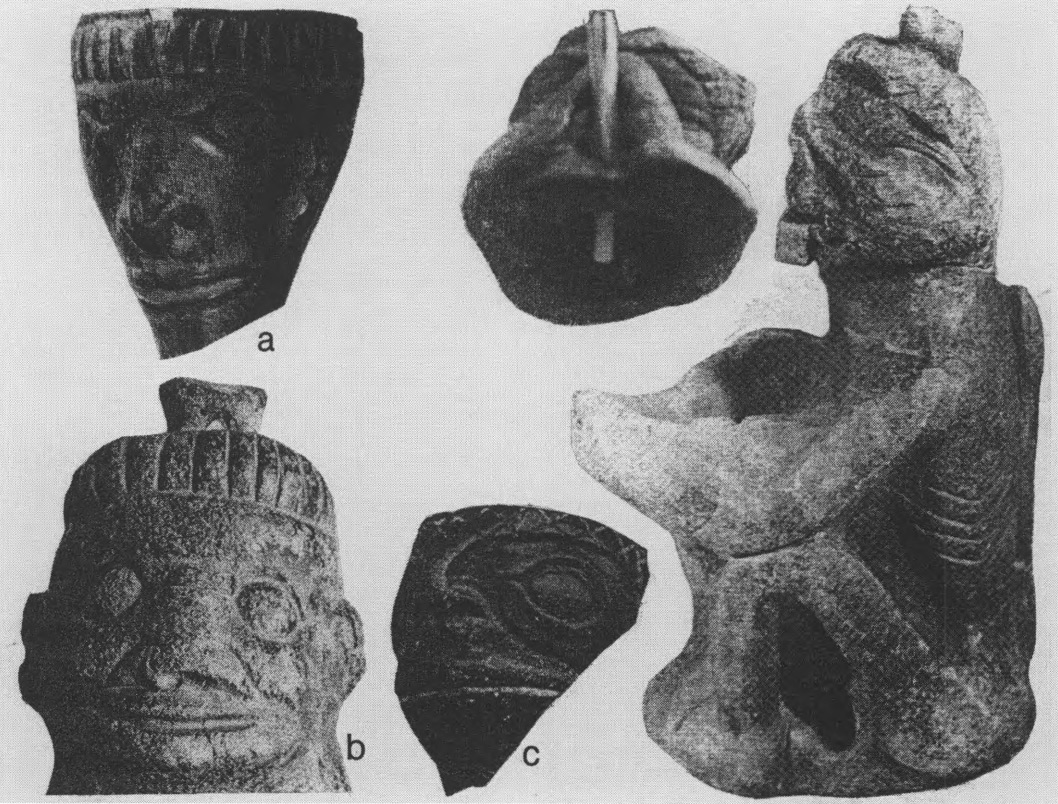
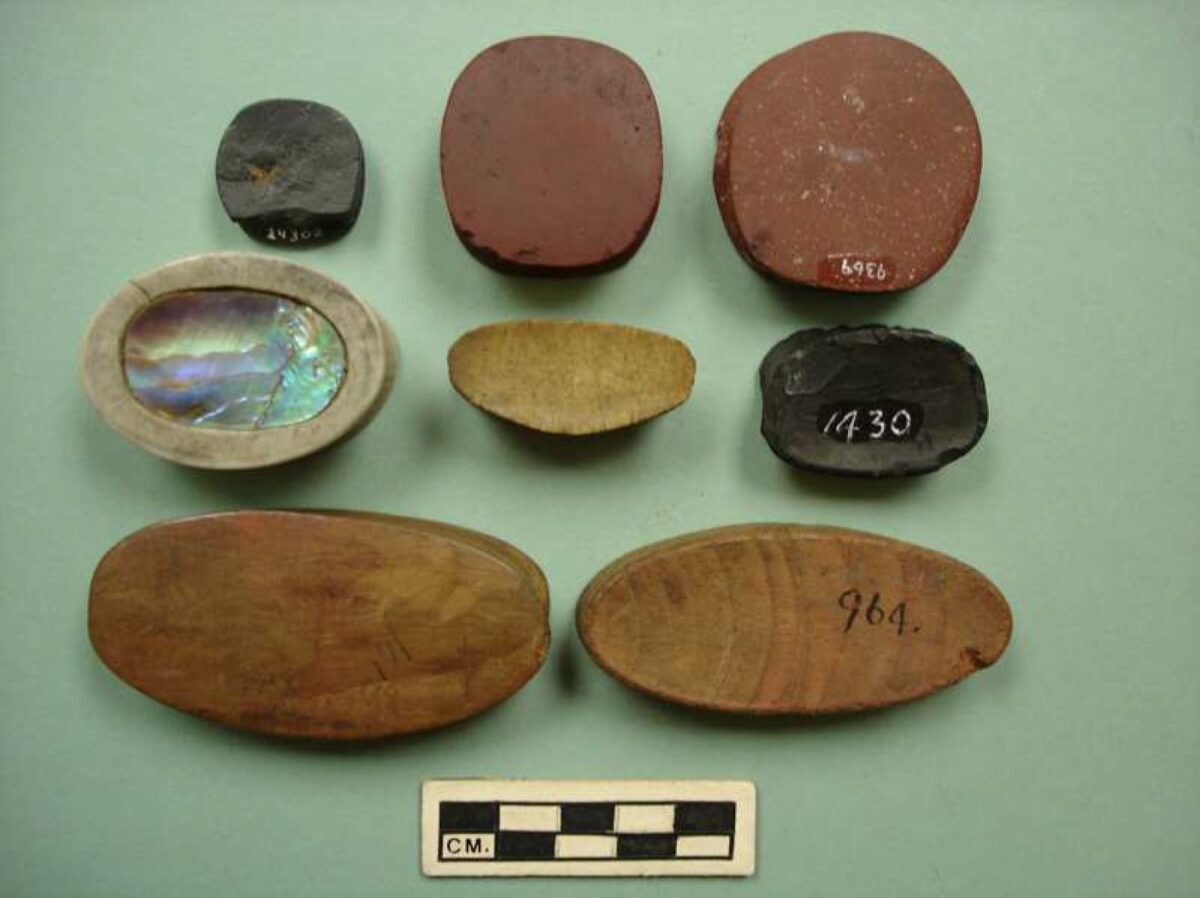
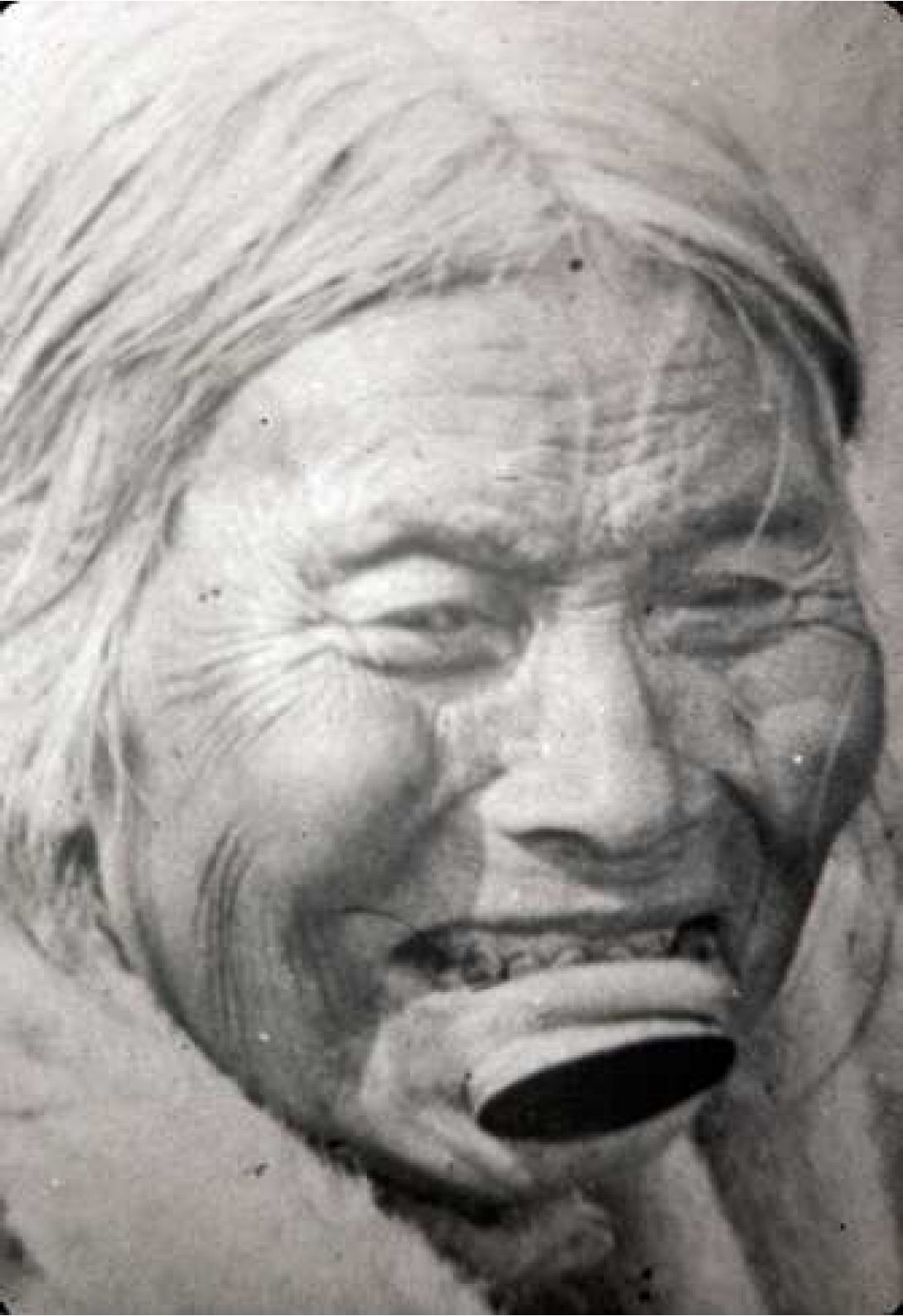
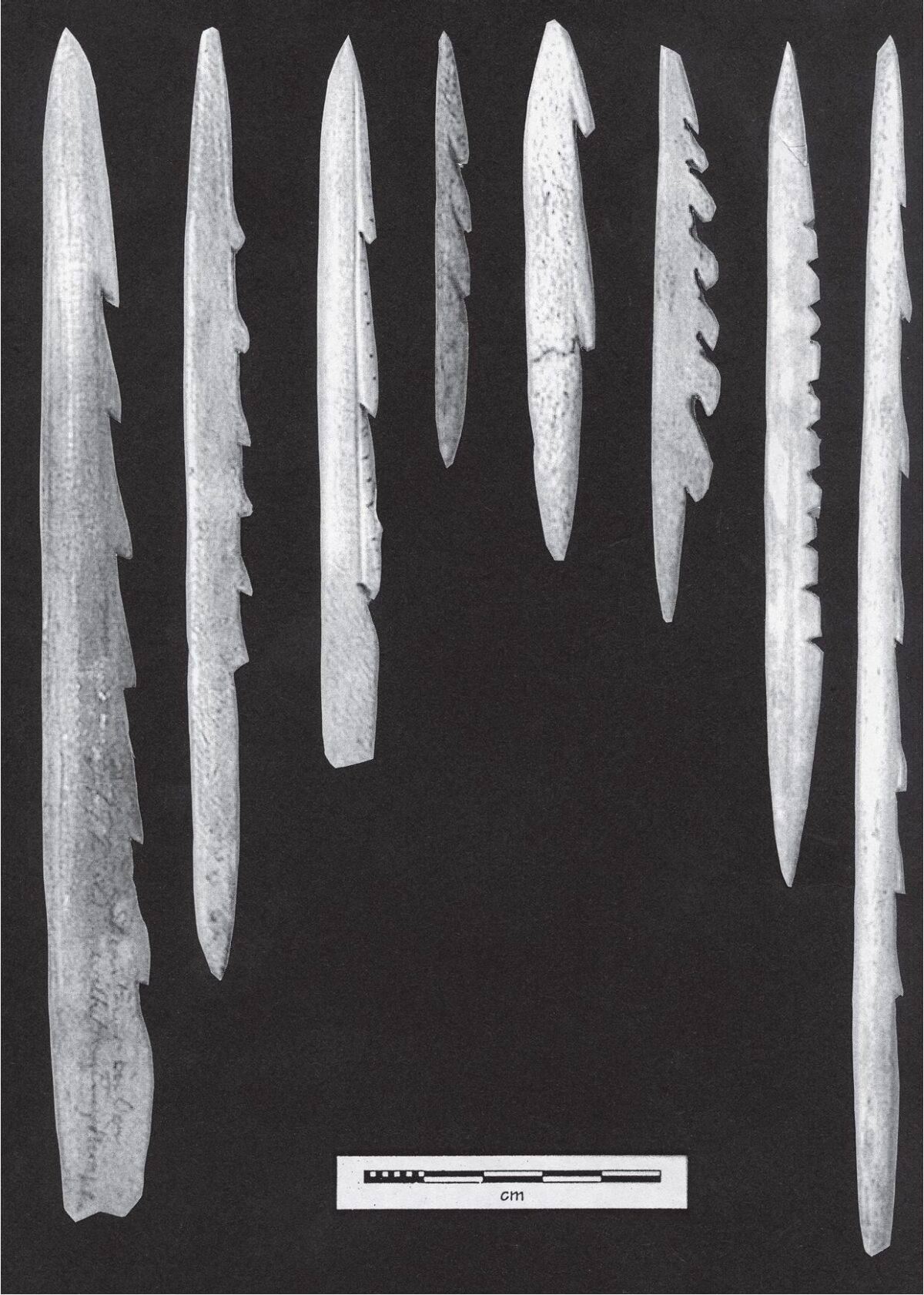
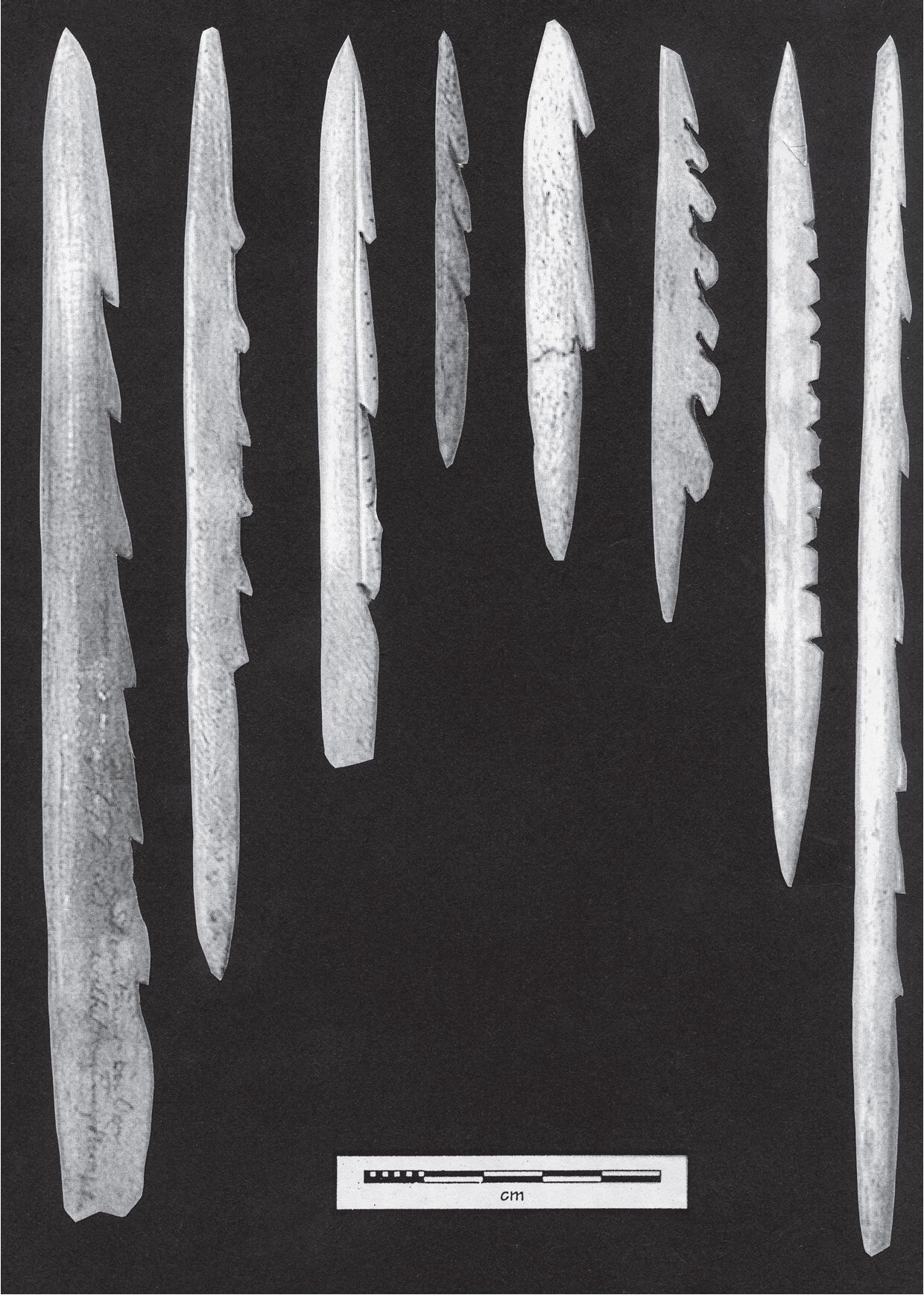
2006. By Grant Keddie This article documents both the historical and archaeological evidence for the movement of European manufactured iron goods across Canada from the 16th to 18th centuries and overviews the late 18th century accounts of Iron observed in the possession of First Nations in British Columbia. Introduction It is a commonly held belief that iron was not used by aboriginal peoples of British Columbia before the arrival of Europeans in the late 18th century. The evidence indicates that this is not the case. The following is an overview of the evidence for the movement of iron from various directions toward British Columbia in the period before European contact and during the very early contact period. After 1799 the … Continue reading “The Early Introduction of Iron Among the First Nations of British Columbia”