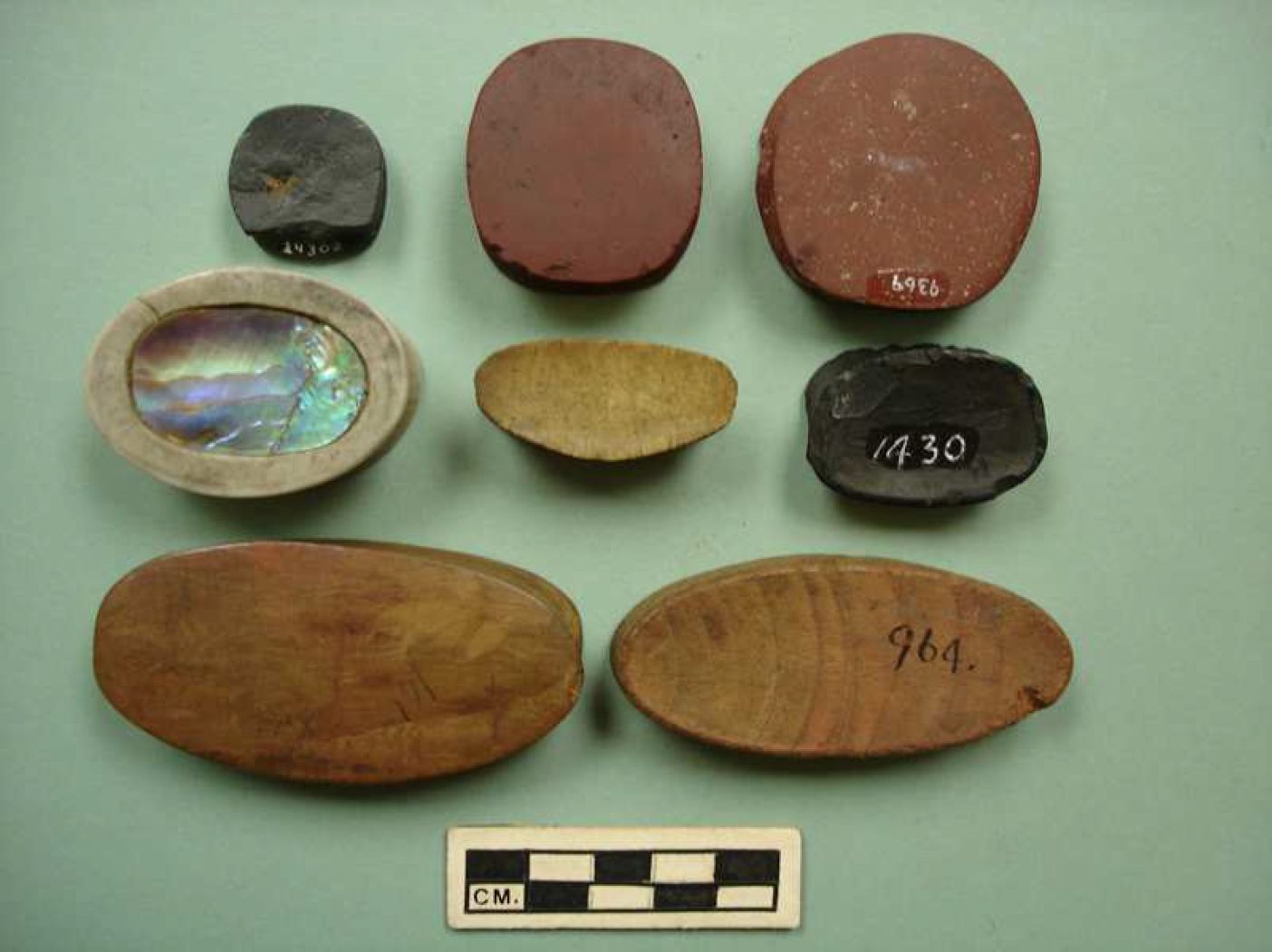
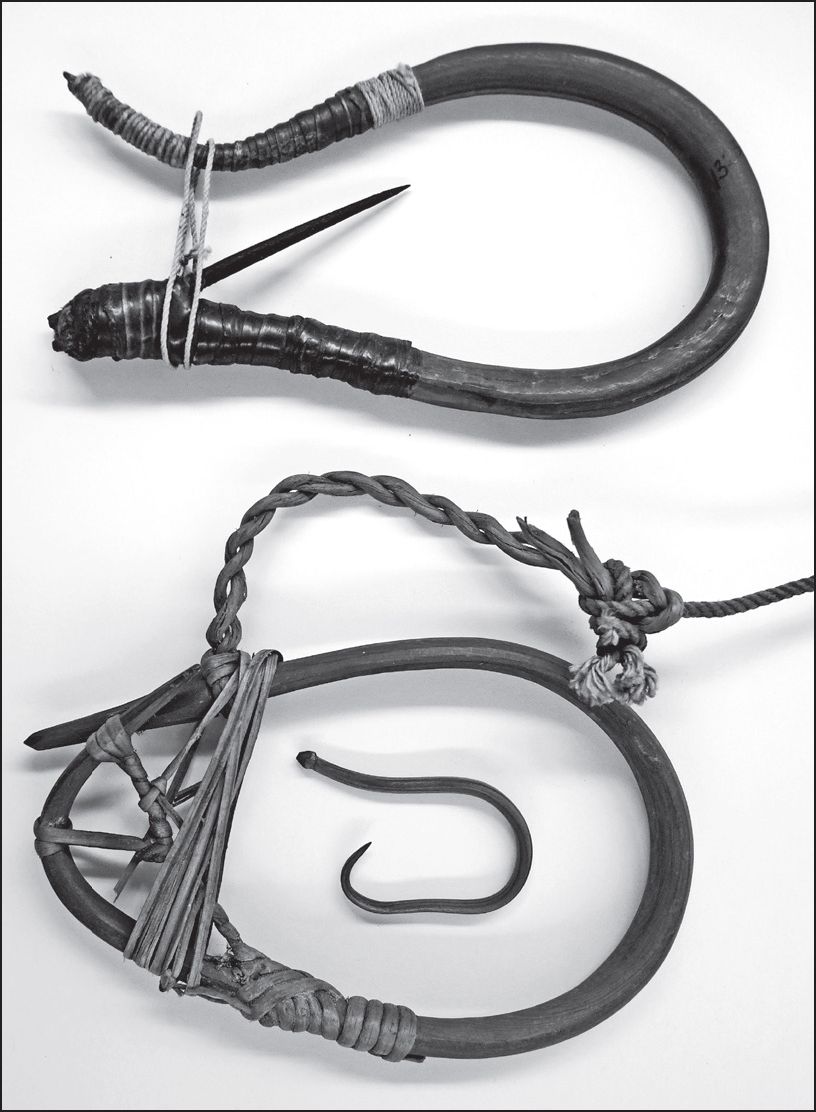
Preface “Carcass butchery is a culturally mediated behavior that reflects the technological, social, economic and ecological factors that influence human diet and foodways. Butchery behavior can thus reveal a great deal about the lives of past peoples” (Egeland et. al. 2024). Egeland. et.al., examined 236 studies on butchery, published between 1860 and 2021, to observe trends. This involved both studies that involved the reconstruction of ethological knowledge and archaeological evidence. The majority of these were undertaken on large bovids. The authors were interested in making recommendations for future studies. They note that one should look for evidence such as: “cut mark frequences on carcasses of different body sizes and taxon”. Part of this study looked at factors such as what … Continue reading “Butchering Sea Lions with Stone Tools”