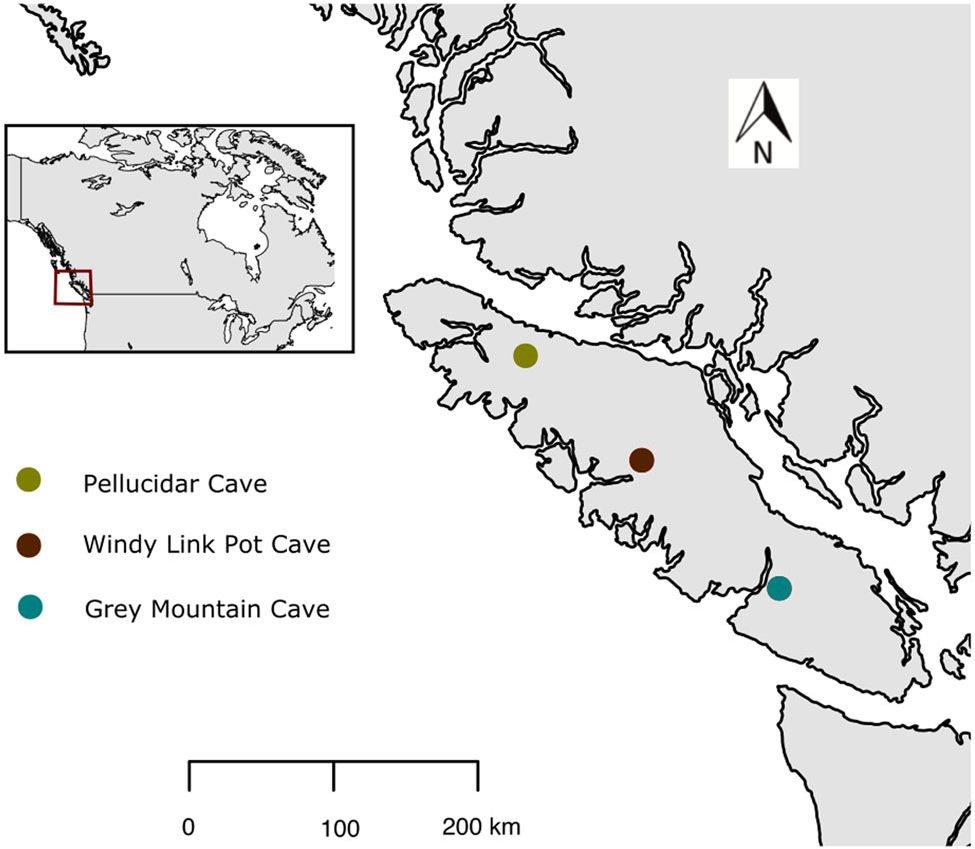
2005. By Grant Keddie (1) c. 1826-27 Census. Census of Indian Population compiled by Archibald McDonald, Fort Langley. In: Report to the Governor and Council, Feb. 25, 1830. H.B. Co. Archives, Provincial Archives of Manitoba, Winnipeg, D.4/123. Pub. 1979. In: The History of Fort Langley, 1827-96, by Mark K. Cullen, as Appendix A. Canadian Historic Sites: Occasional Papers in Archaeology and History, Paper No. 20, National Historic Parks and Sites, Ottawa. The list for “Vancouver’s Island” moves geographically from the “Nanemoos” (Nanaimo) with 100 men; the “Cowaitchins” (Cowichan) with 200 men; the Sanutch (Saanich) with 60 men; the Tchanmus (Songhees) with 40 men; to the “Soaks” (Sooke) with 50 men. There is no mention of Klallam on Vancouver Island. The … Continue reading “List and comments on Select Population References to the Lekungen (Songhees and Esquimalt Nations)”