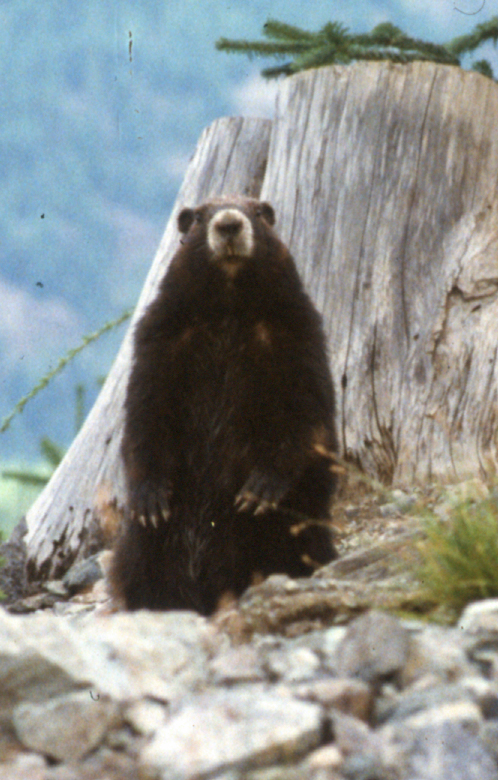
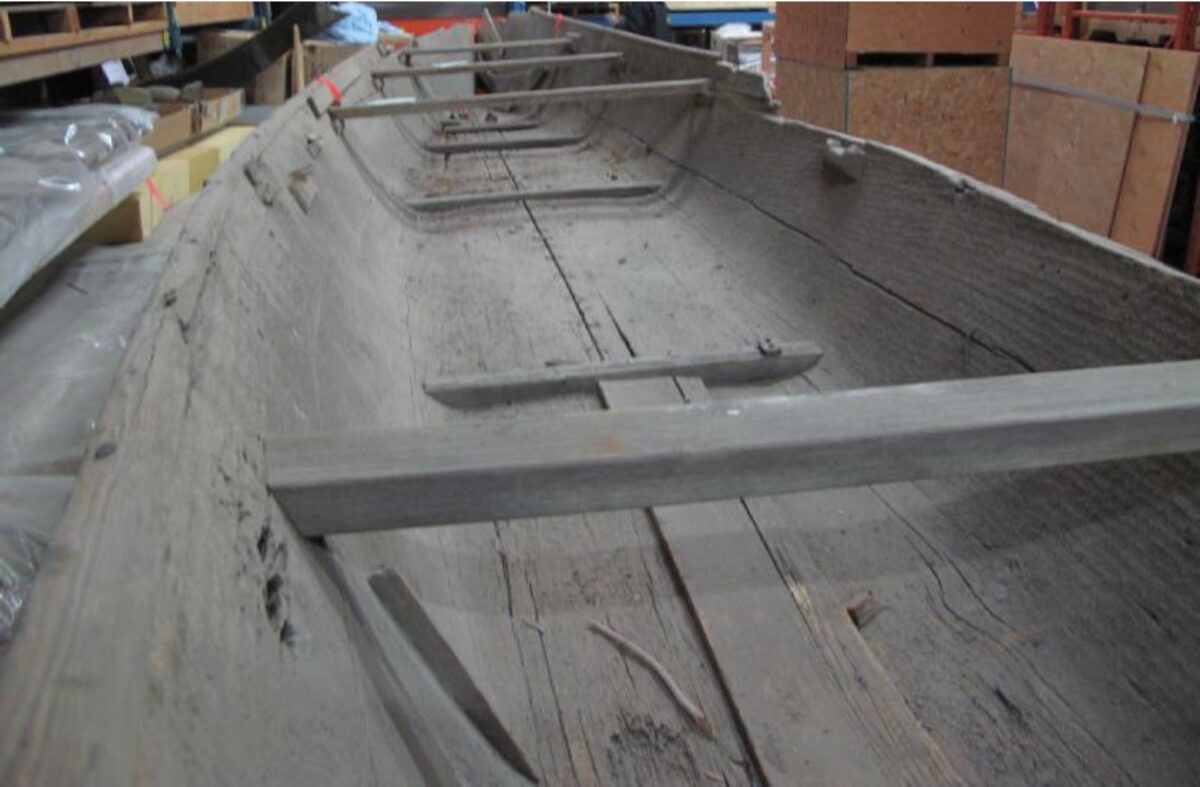
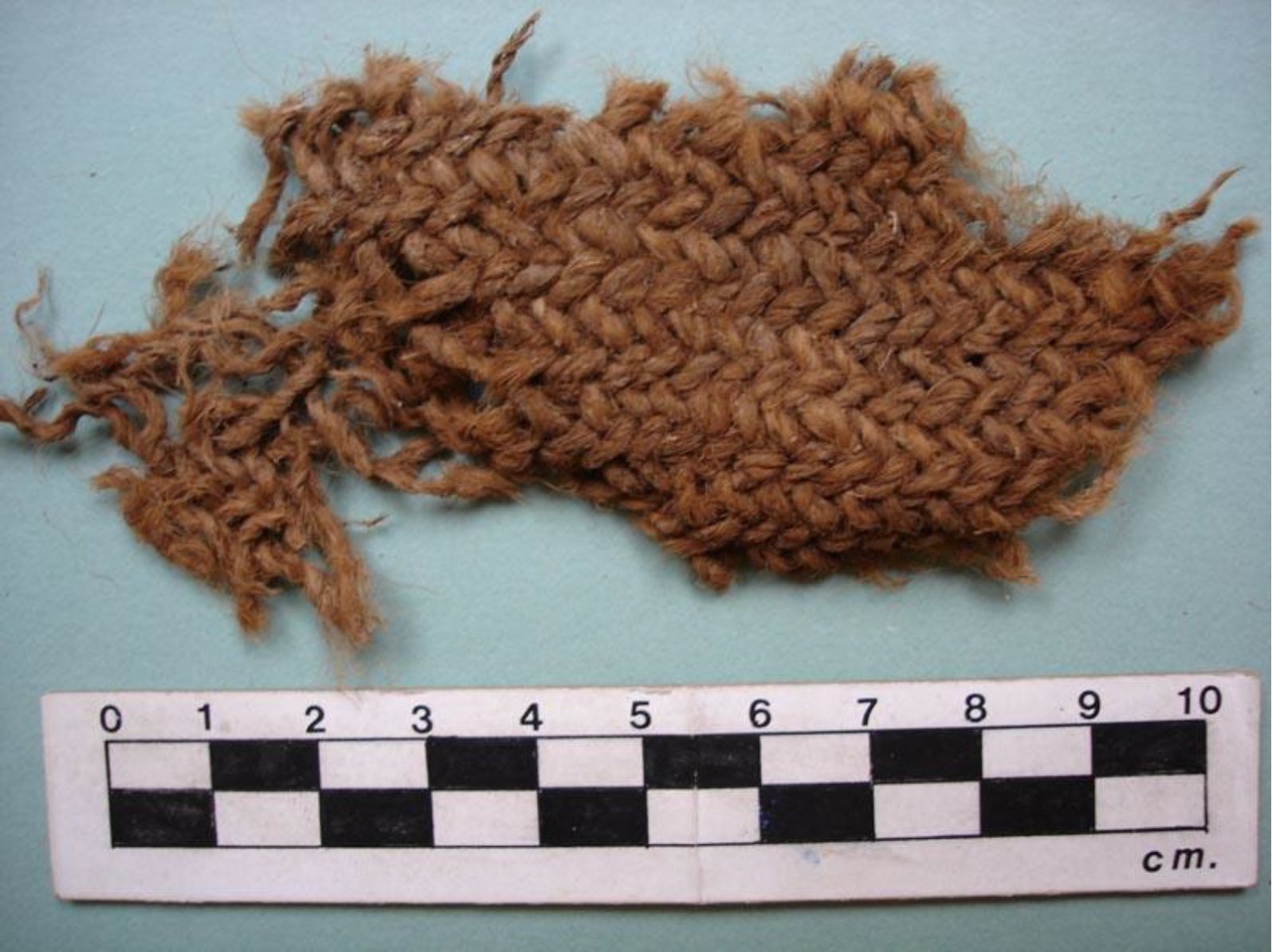
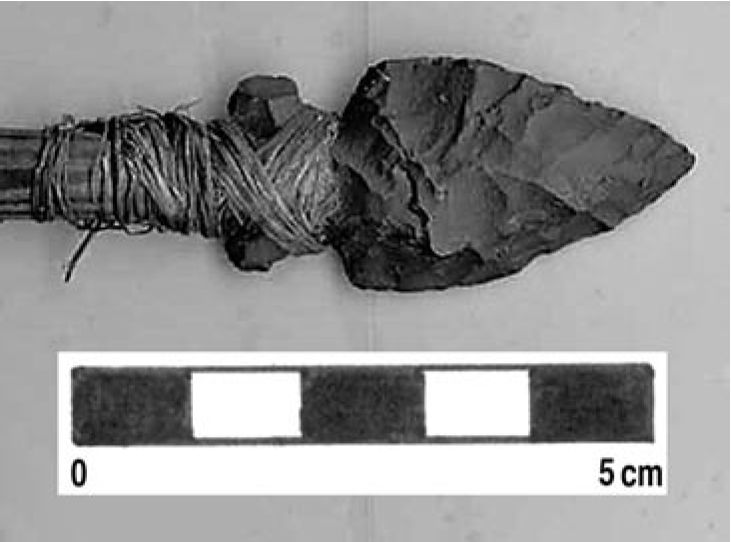
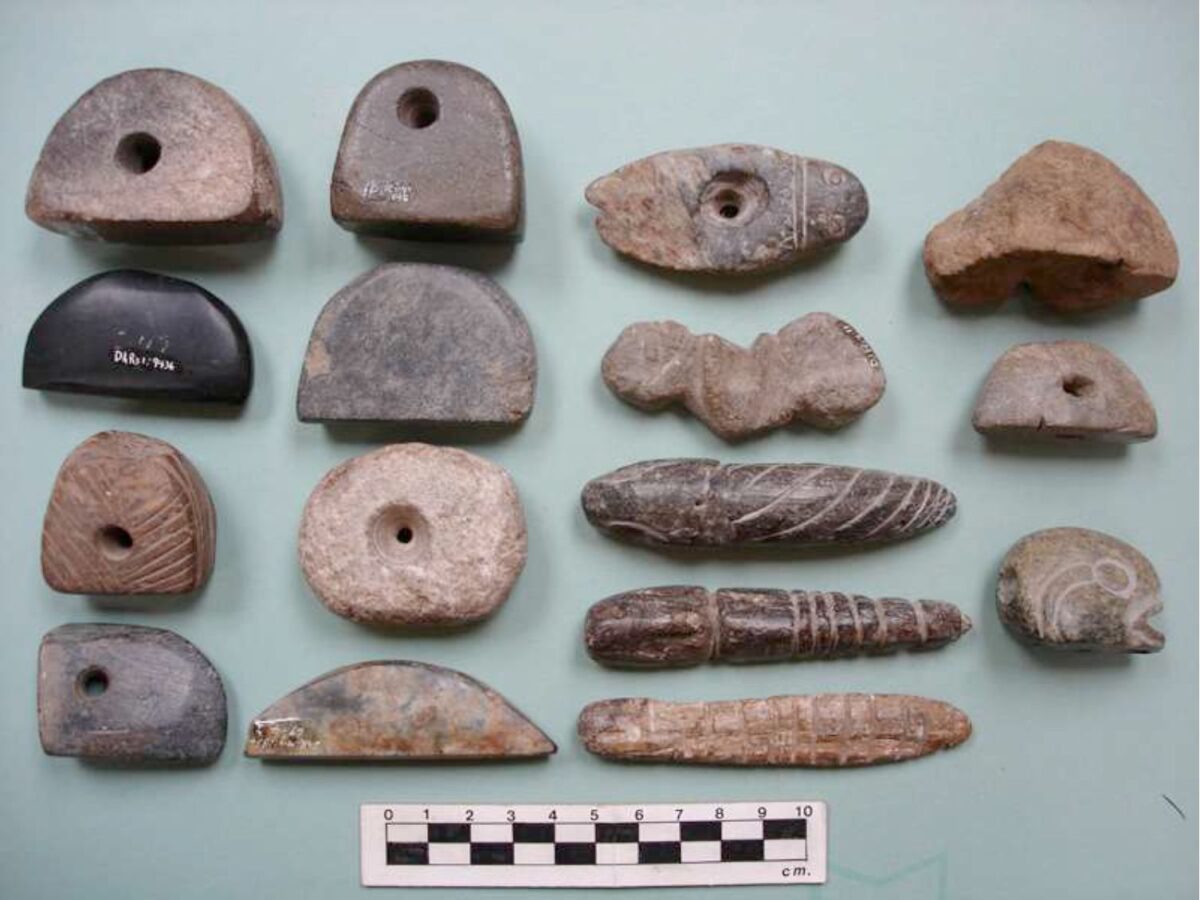
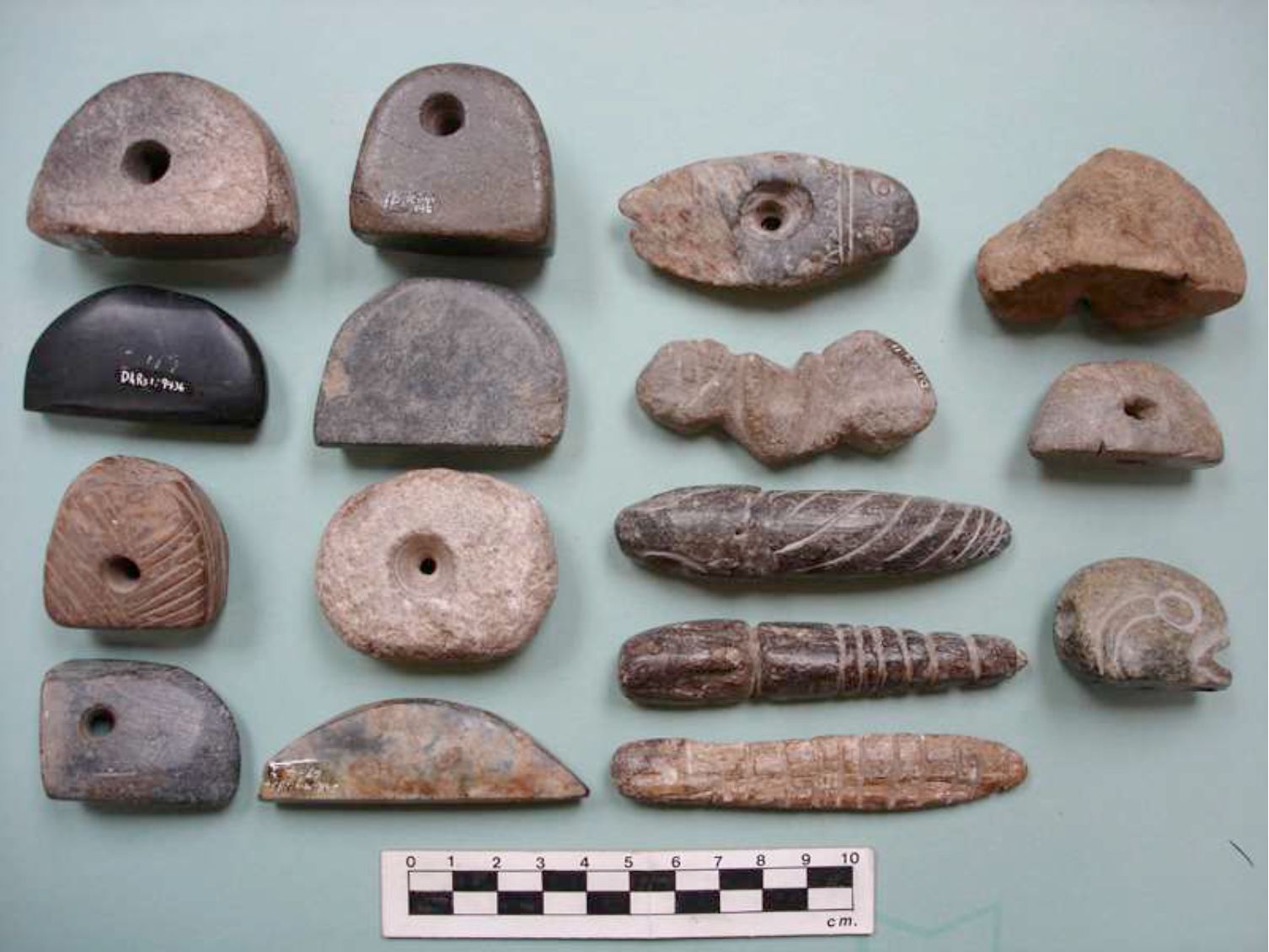
May 28, 2019. By Grant Keddie. Introduction Marmots were hunted in many parts of British Columbia for their furs and their fat content. Both Coastal and Interior peoples went into the mountains every fall to hunt them. Some First Nations continue to hunt marmots. See Appendix 1, First Peoples and Marmots of British Columbia, for a detailed overview of the role of marmots in Indigenous societies. Deadfall traps and snares of various sizes were used for catching most species of mammals as well as birds. There are several types and sizes of artifacts in this general category of trap devices that were used by the Tlingit and their inland relatives for trapping mainly marmots and ground squirrels. Small deadfall trap … Continue reading “Marmot Trap Triggers in the Royal B.C. Museum Ethnology Collection”