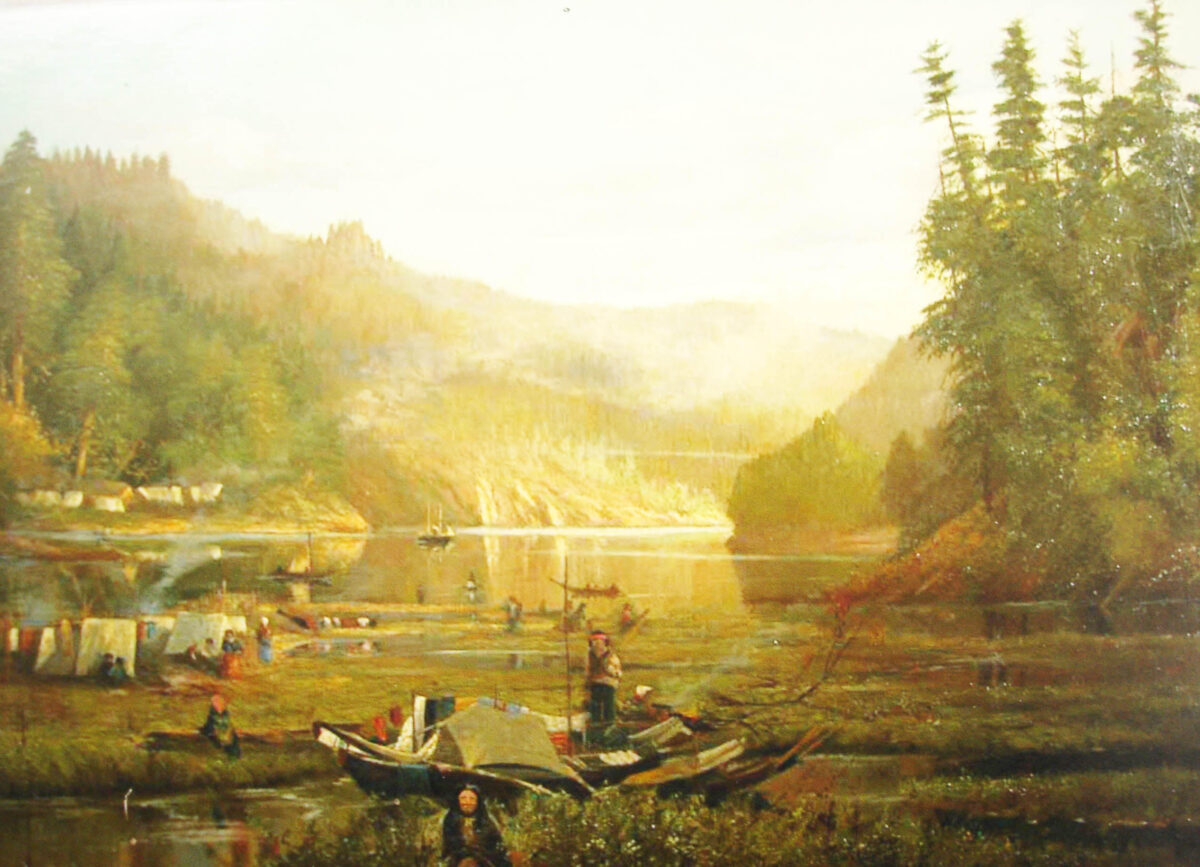
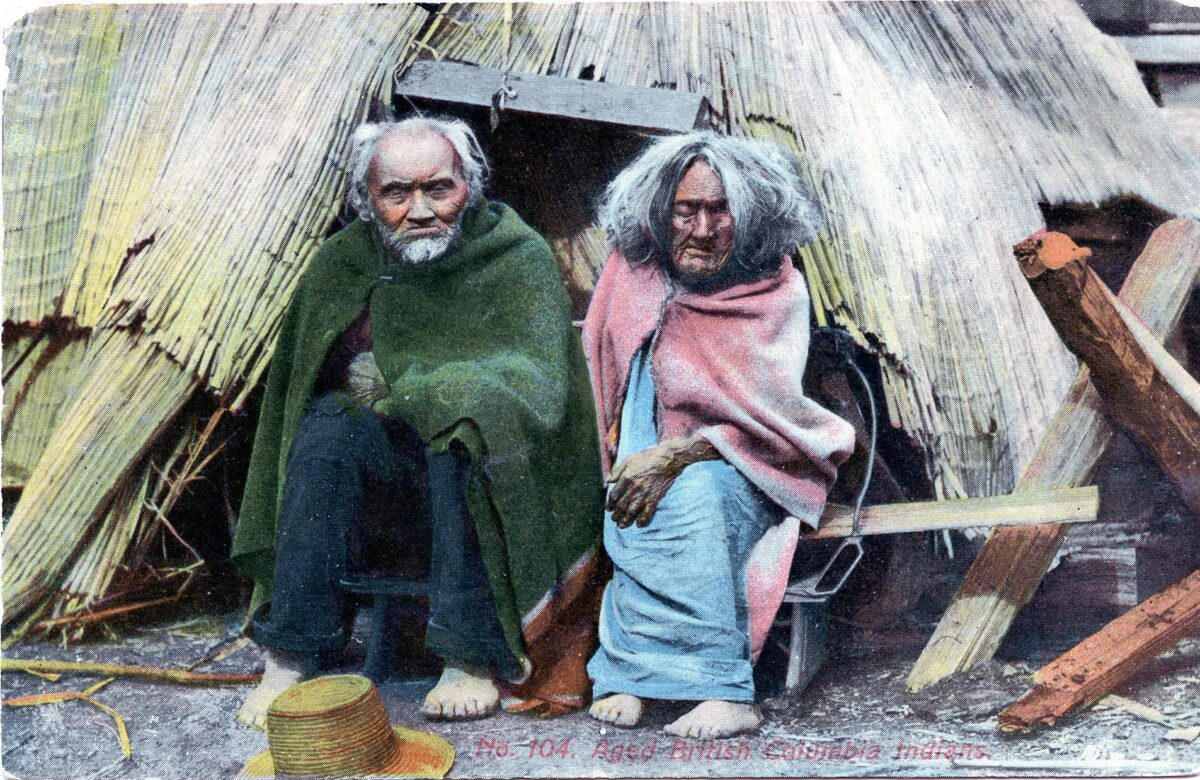
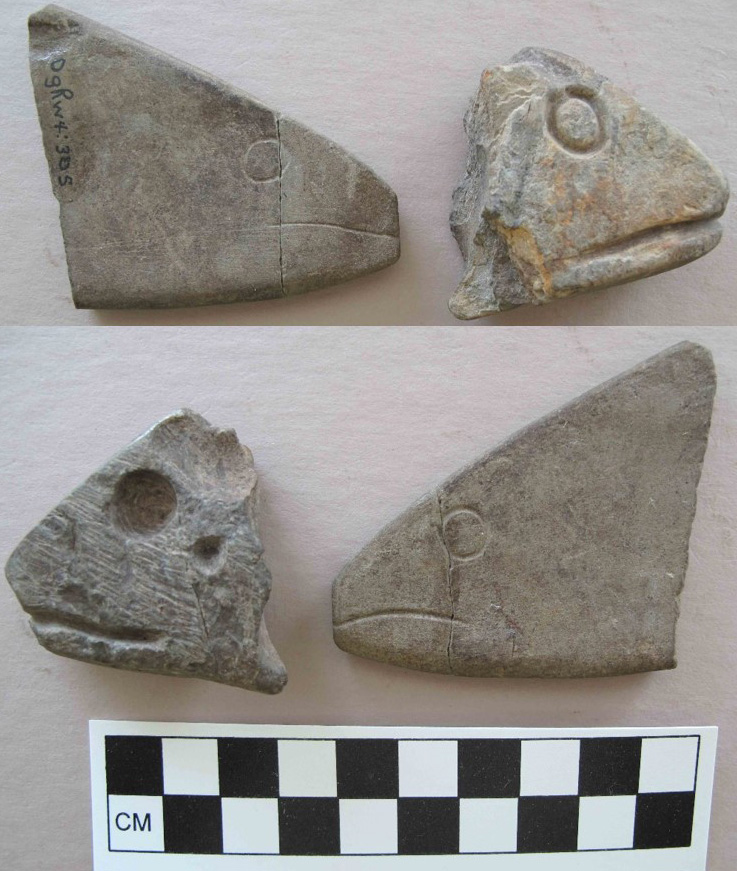
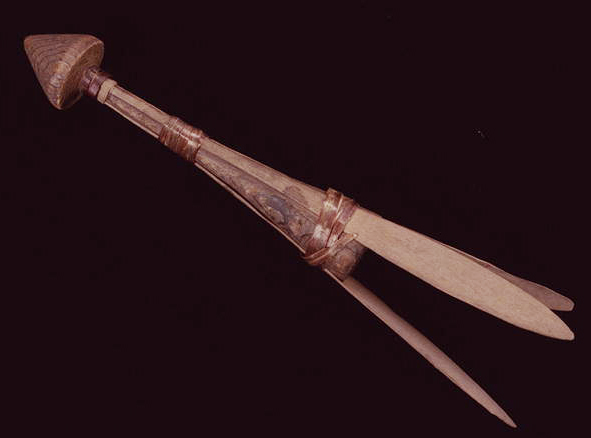
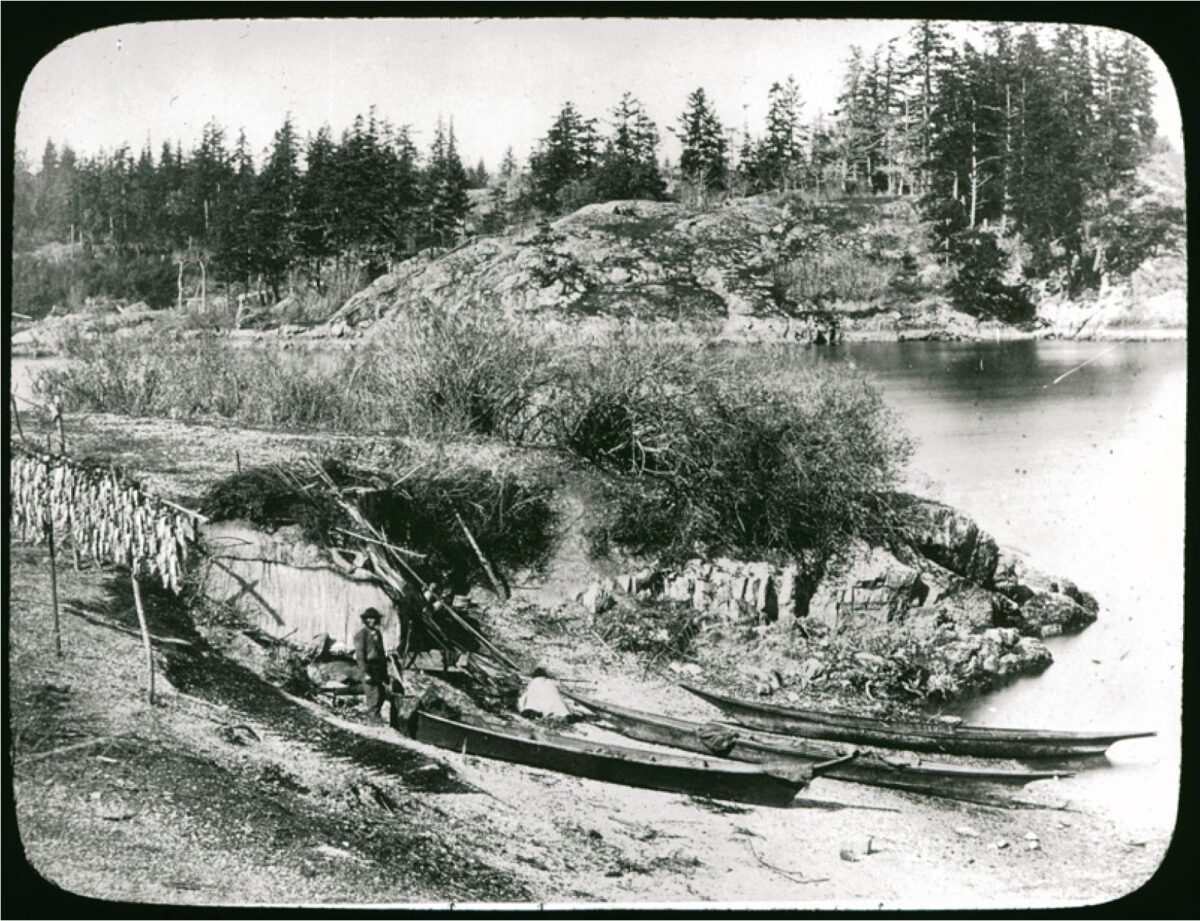
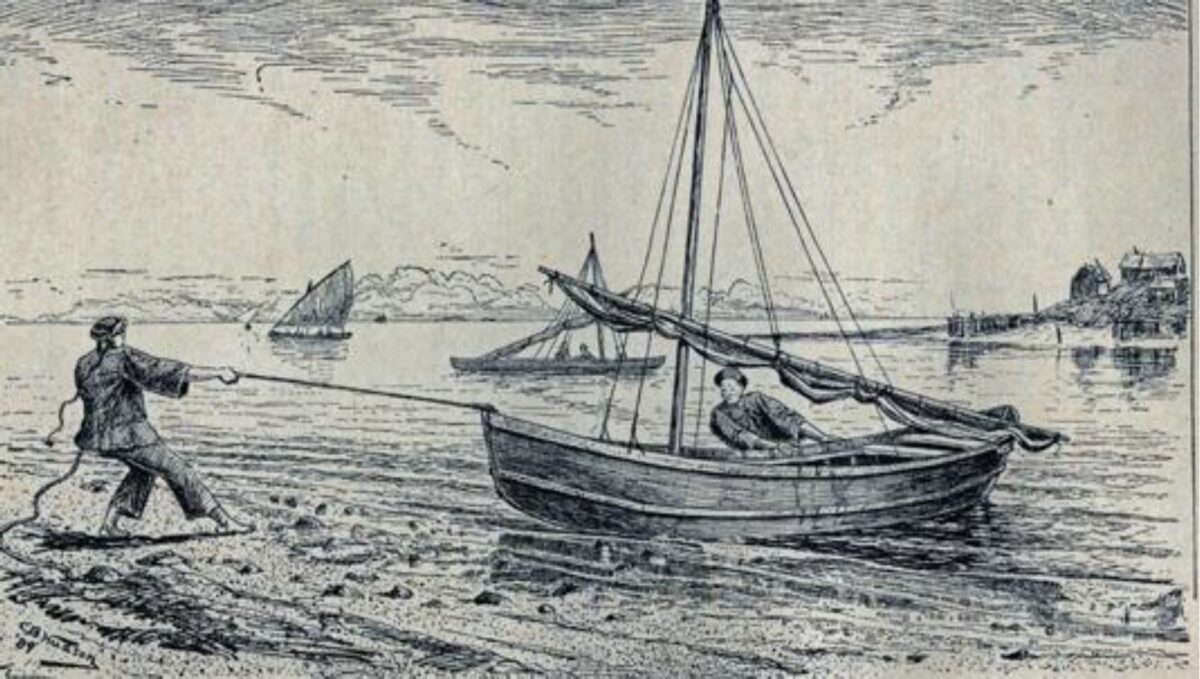
Stinging Nettle, in various species of the genus Urtica, was an important resource for Indigenous people across the northern hemisphere of the planet. Its new shoots were eaten in the spring as a source of vitamins and minerals and the string made from its stalk was used to make everything from nets to the foundations for light clothing. See Skoglund et. al (2025) for overview of European usage. As stinging nettle needs partial shade and mineral rich soil that contains potassium and uric acid, it grows profusely on the cultural deposits built up at old village sites. The importance of nettle (Urtica dioica) in southern British Columbia is made clear in letters between James Douglas and the Hudson’s Bay company … Continue reading “Stinging Nettle. Indigenous Processing and Use”