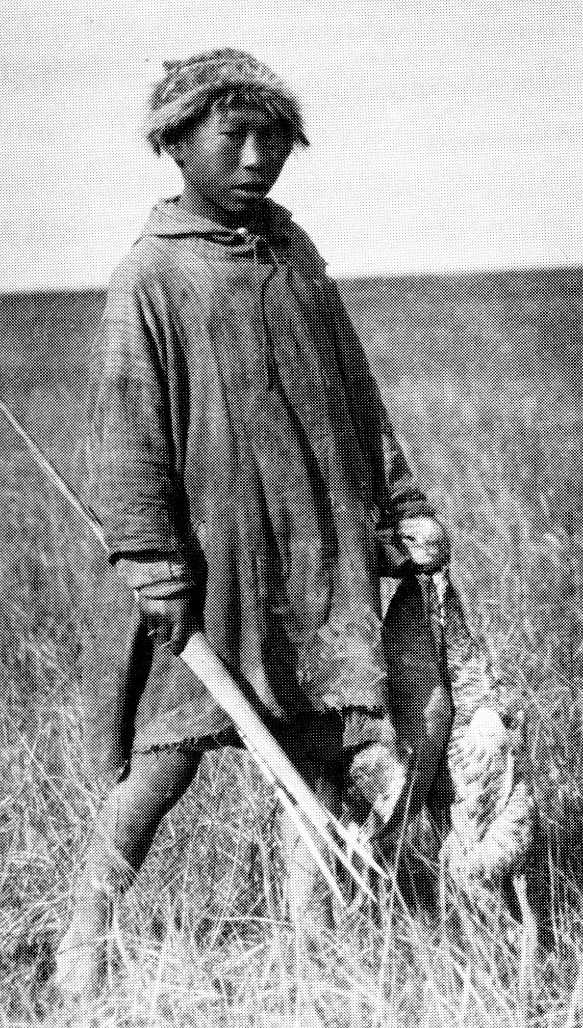
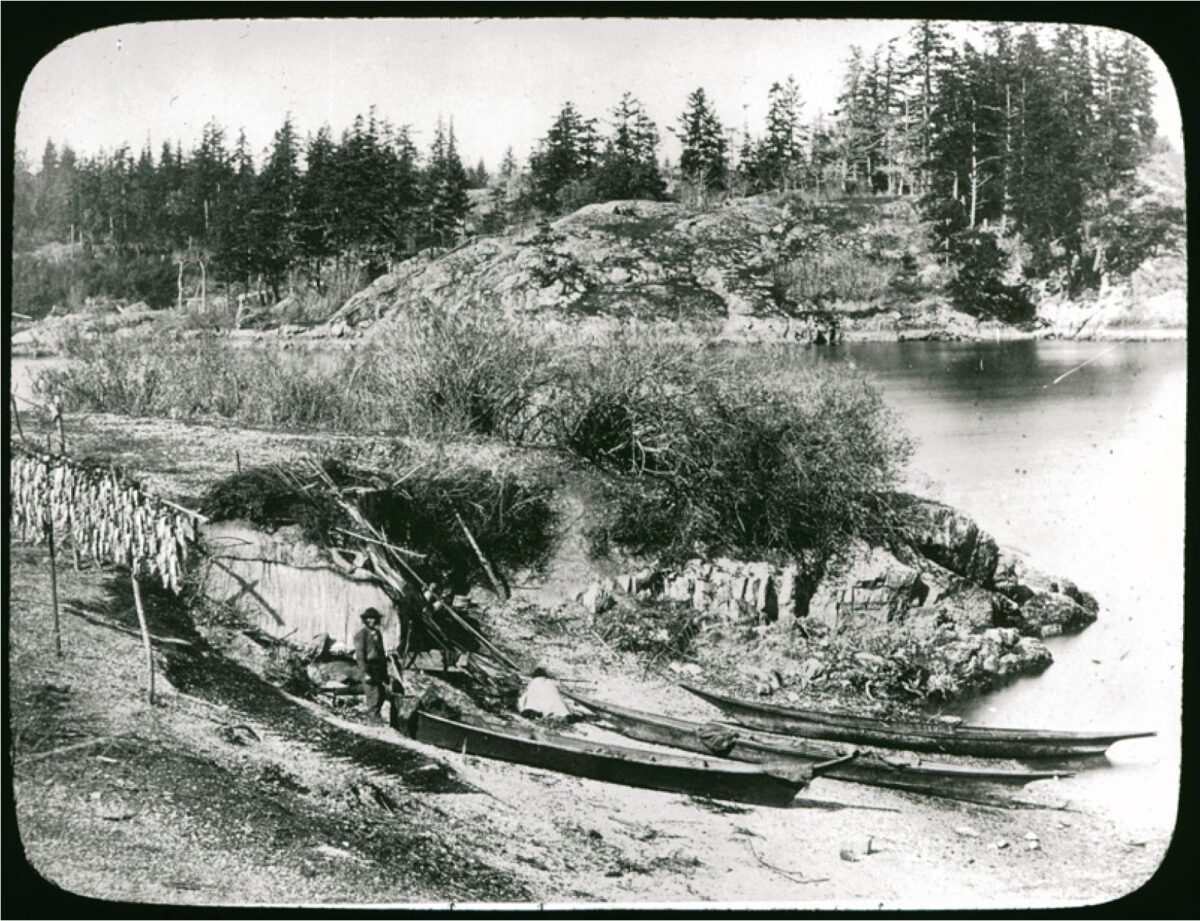
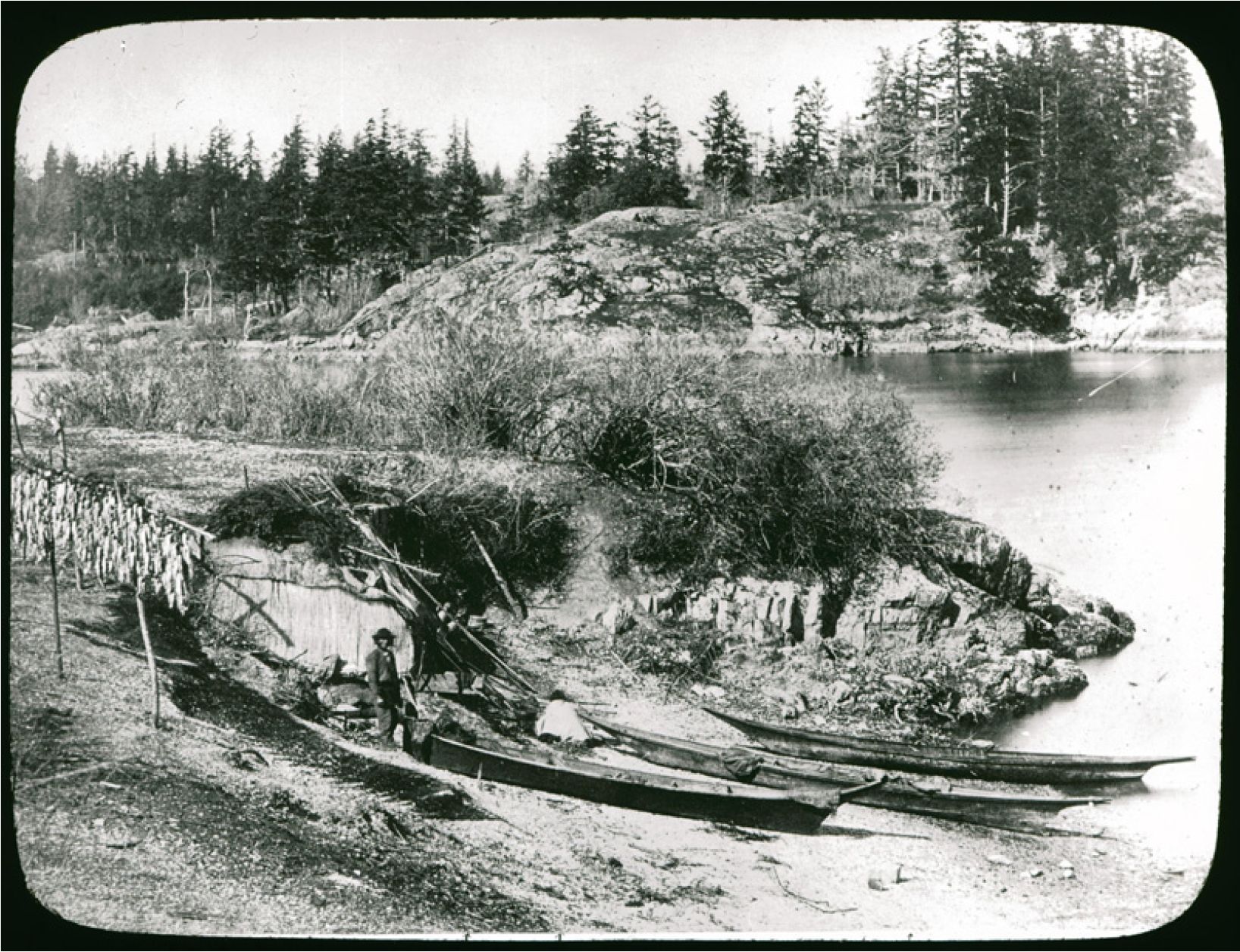
By Grant Keddie. In 1941, World War II was on. At the age of 72, Jimmy Fraser (Kin-Kay-nun; Unthame, Cheachlacth) of the Songhees Nation, stood next to his fellow band members Jack Dick, Roddy Stewart, Art Hall, Clarence Dick, Richard Albany, Dave Fallardeau and Louis Kamai, at the Esquimalt dock yards, famous for their ship building. The Songhees were being praised for their contribution to the war effort. Like so many other Indigenous people then and before in World War 1, they contributed to the Canadian war effort. The Songhees were being singled out for the work they were doing at the dock yards. The foreman at the dockyards said the Songhees “were the best workers he ever had”. (Colonist … Continue reading “Jimmy Fraser the Songhees Story Teller”