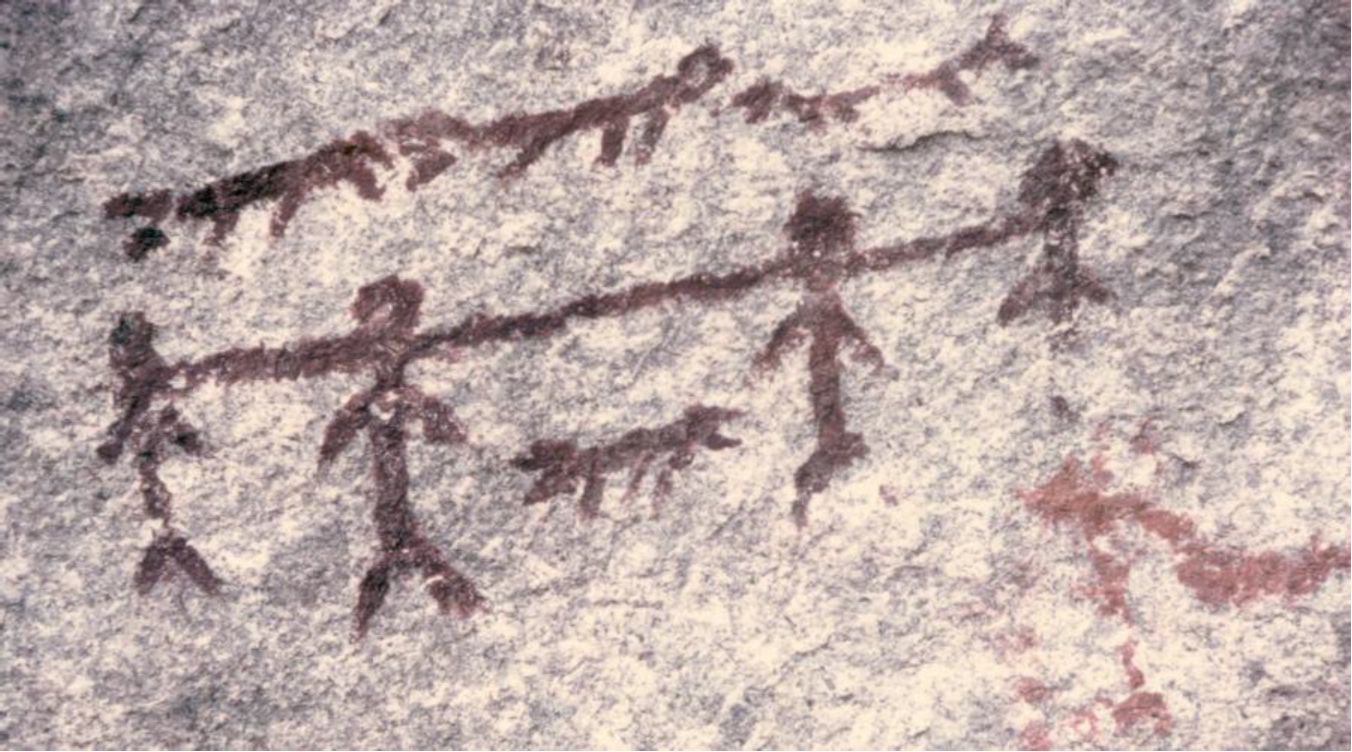
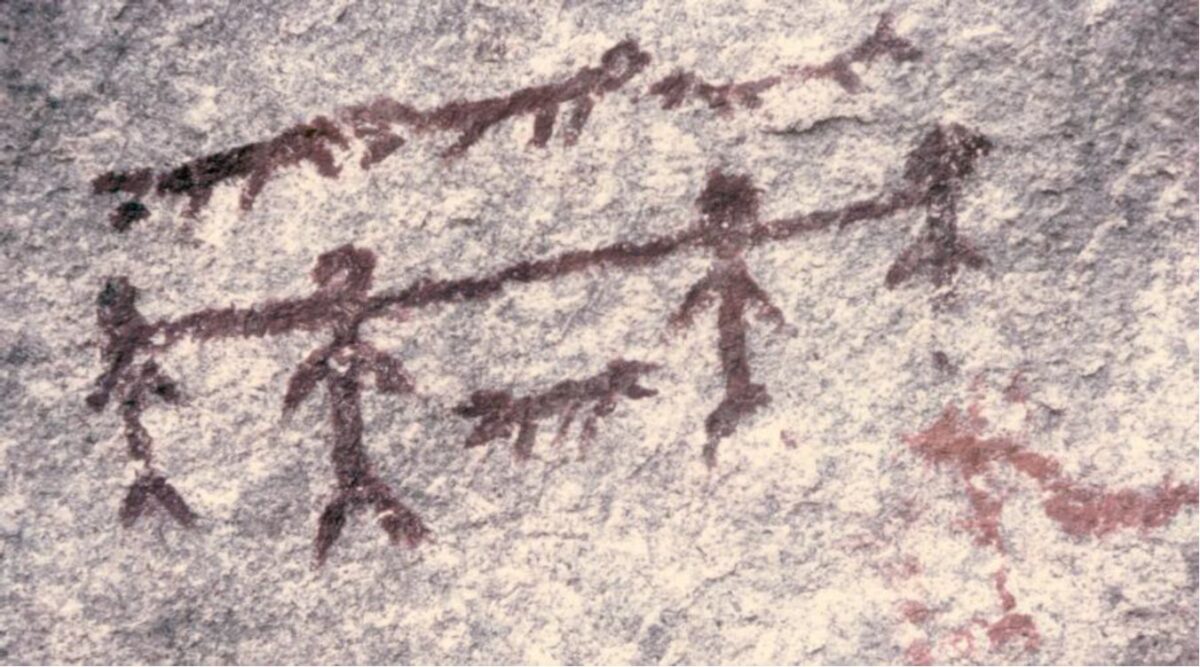
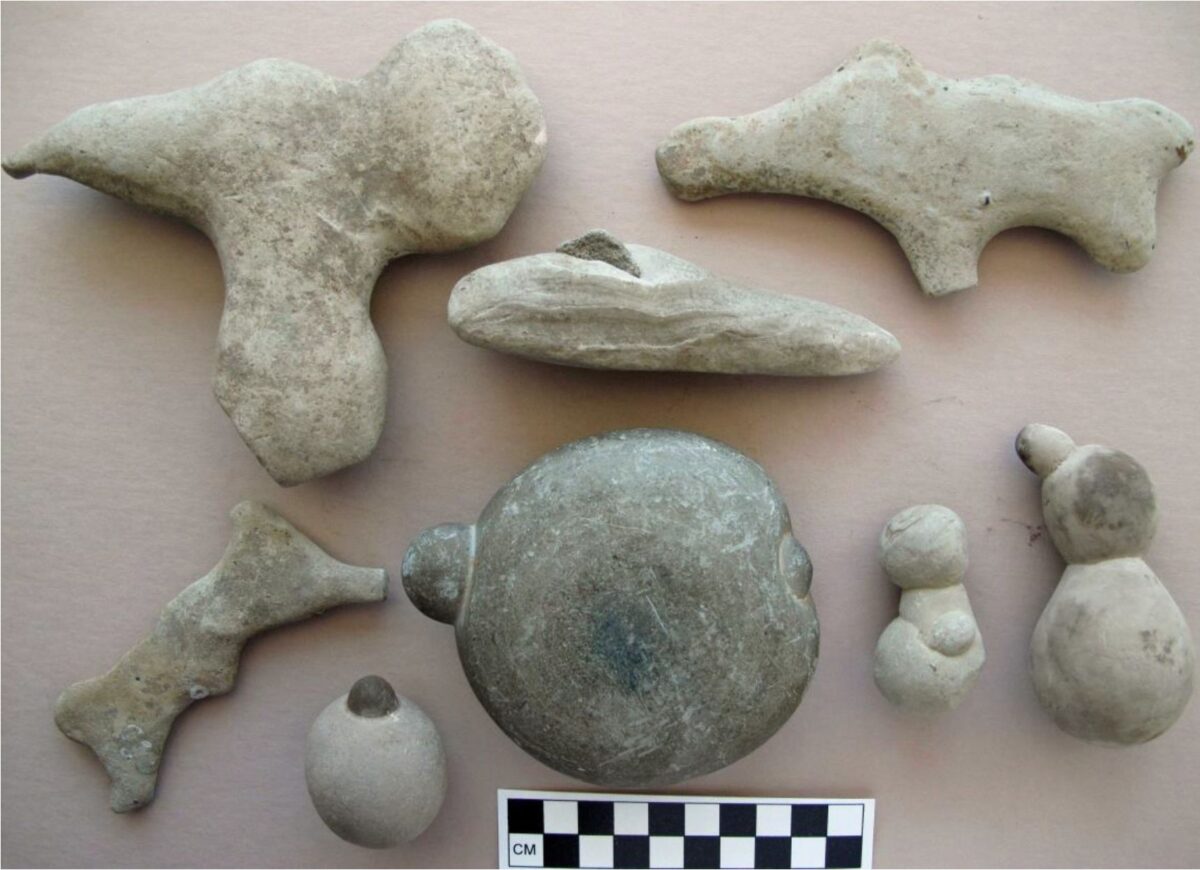
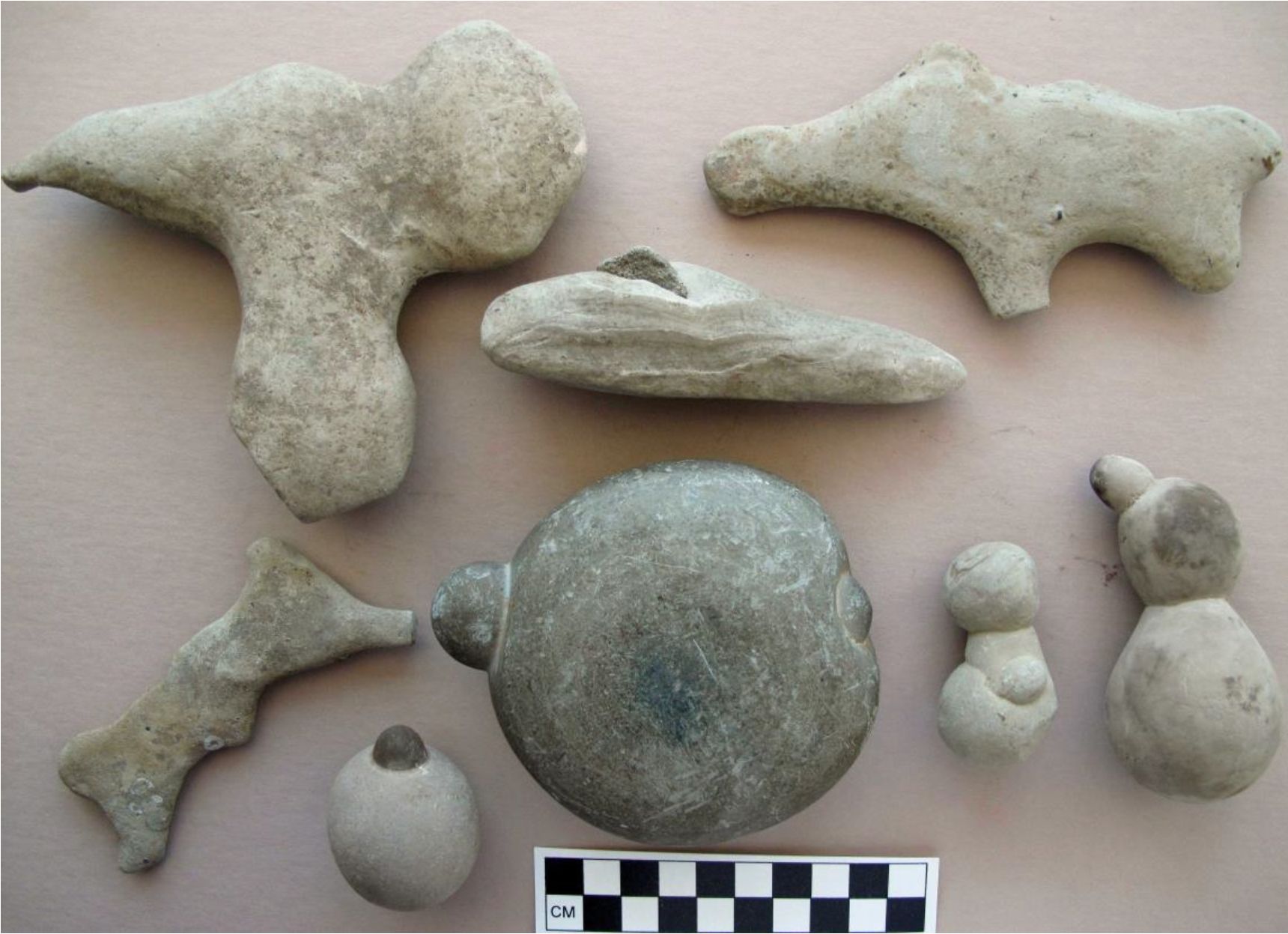
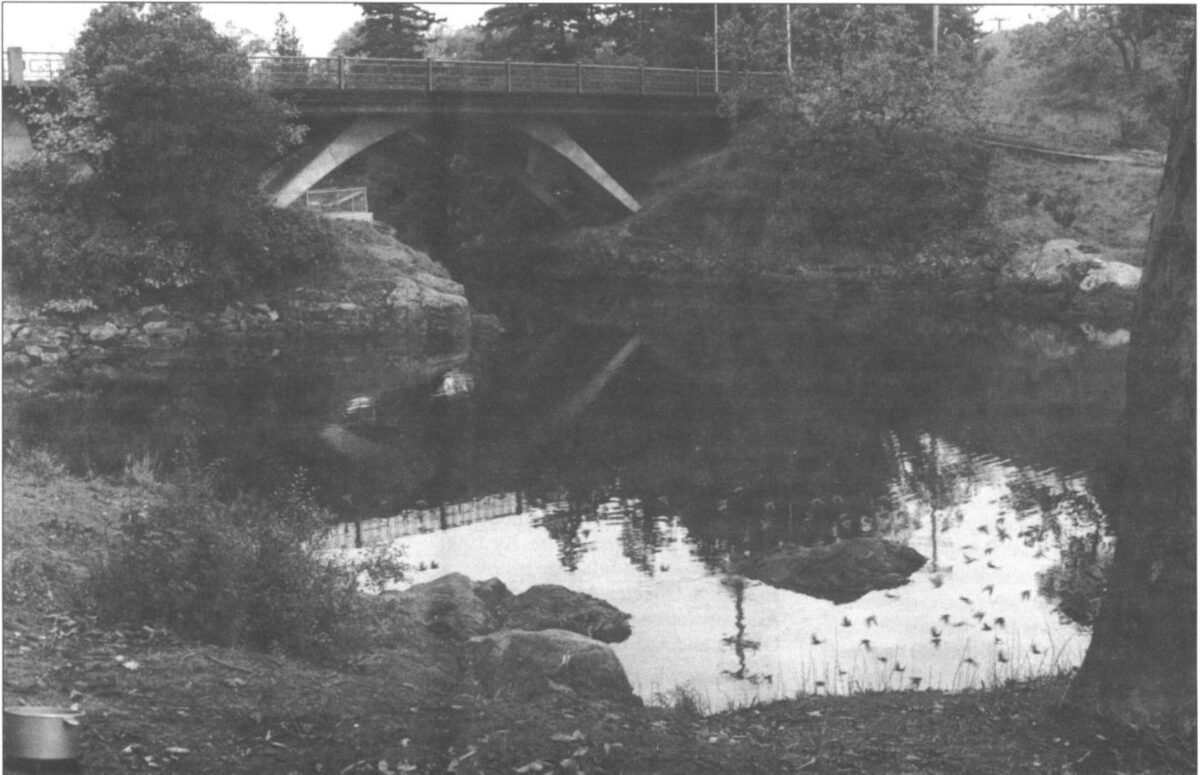
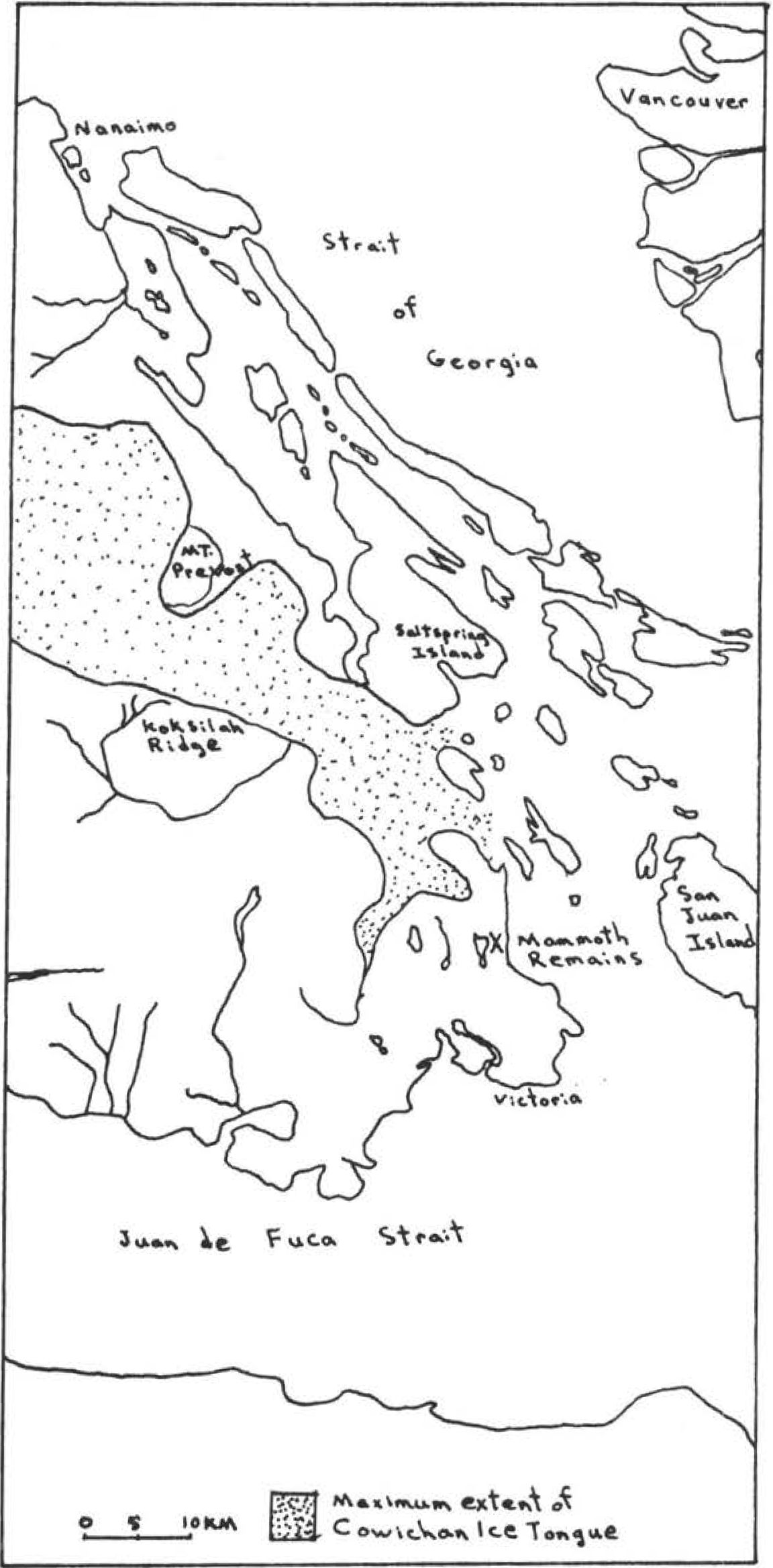
2005. By Grant Keddie The Chuchawaytha Rock Shelter Pictographs. Since reading the Midden article by Darius Kruger (2005), I thought I should add some unique information to his favorite ancestral site – the Chuchawaytha Rock Shelter, DhRa-2. This Similkameen region site has been referred to in earlier literature as the Hedley cave site. There has been some confusion regarding this location perpetuated by non-First Nation stories about early visits by Spaniards. Two clusters of images referred to as “the horseback riders” and “the prisoners” have often been misinterpreted by non-First Nations, as a single unit that represents Spaniards on horseback with ropes tied around the necks of a group of First Nation prisoners. This interpretation is an attempt by non-First Nations to fit these images with … Continue reading “Hedley Cave Site DhRa-2”