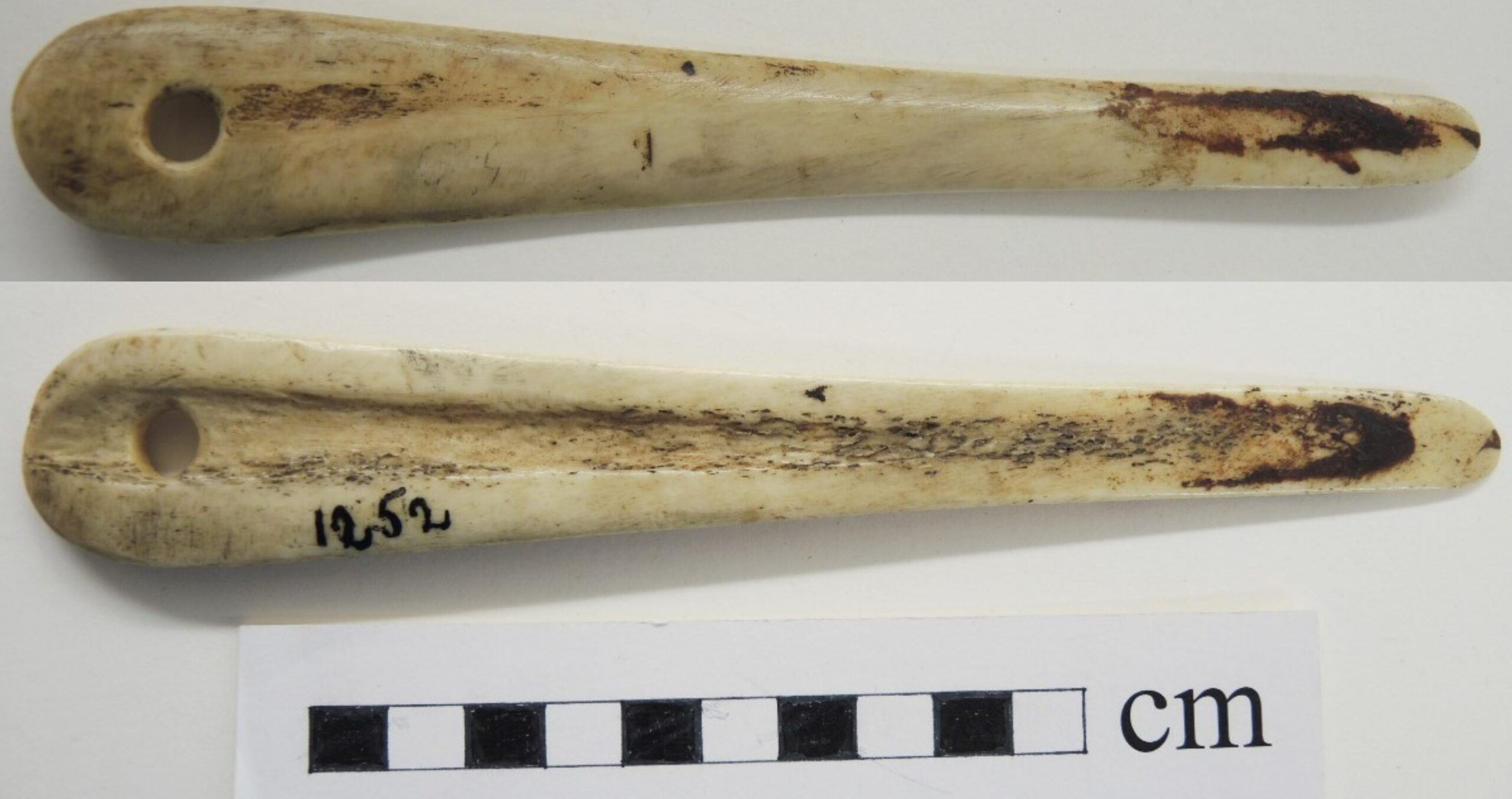
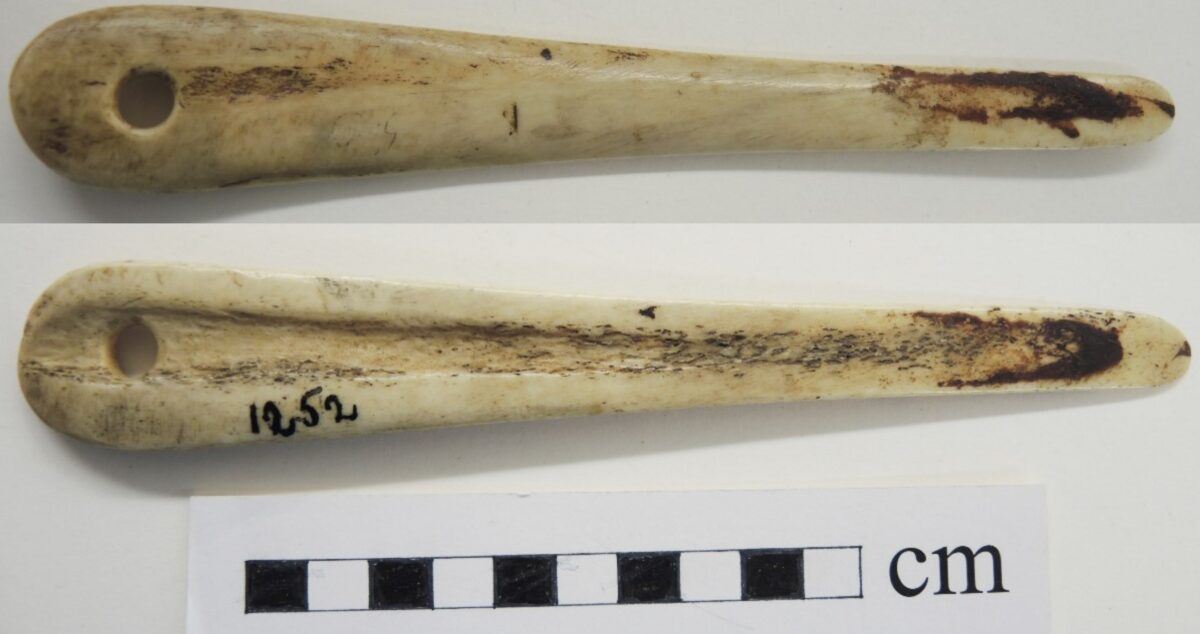
Introduction Many of the artifacts recovered by archaeologists have no ethnographic counterpart in museum collections. Most Indigenous ethnographic artifacts are made of wood. Rarer examples of bone or antler artifacts in ethnographic collections, with documentation, become important to help identify the use of some archaeological artifacts. The Bone Tool One unique artifact, in the Indigenous collections of the Royal B.C. Museum, is a bone tool described as a hat makers’ knife. The example was collected by Kwakwaka’wakw, George Hunt, in 1899, and sold to Charles Newcombe in 1901. Its ethnic origin is identified as Nahwitti, Kwakwaka’wakw. This artifact, number RBCM1252 (old #19074), was listed in the original catalogue by Charles Newcombe as: “Bone knife (Kwetani). Of the mountain goat. Used … Continue reading “A Hat Makers Bone Tool”