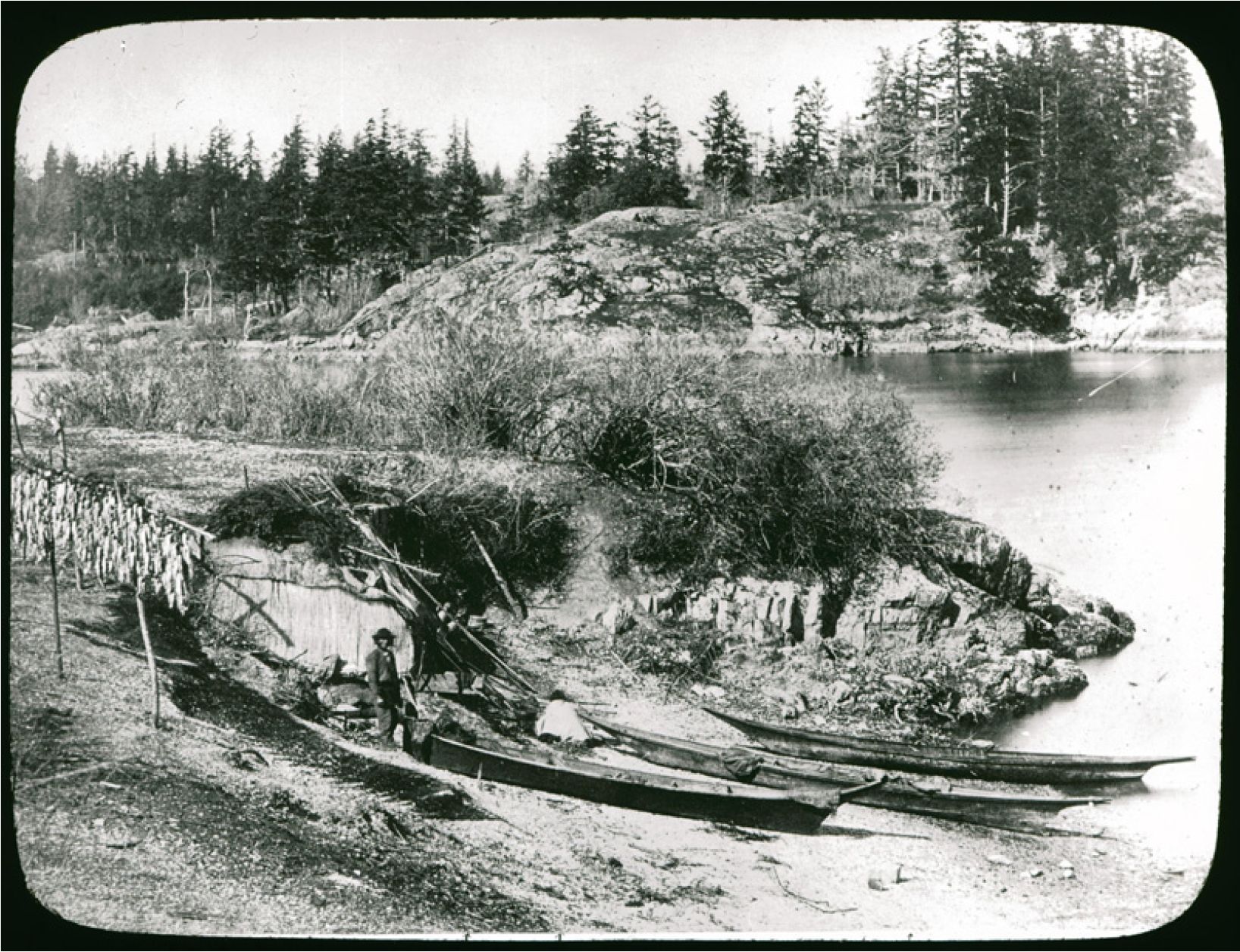
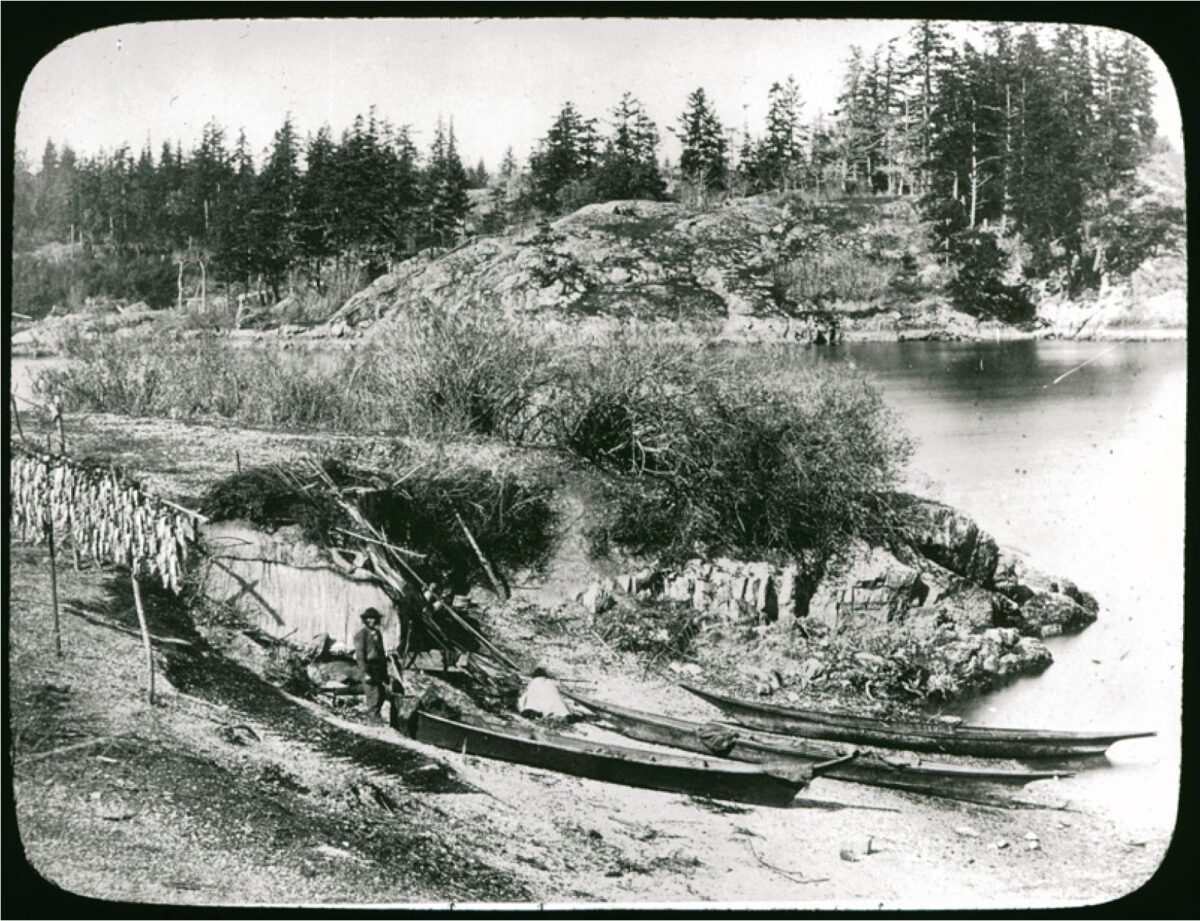
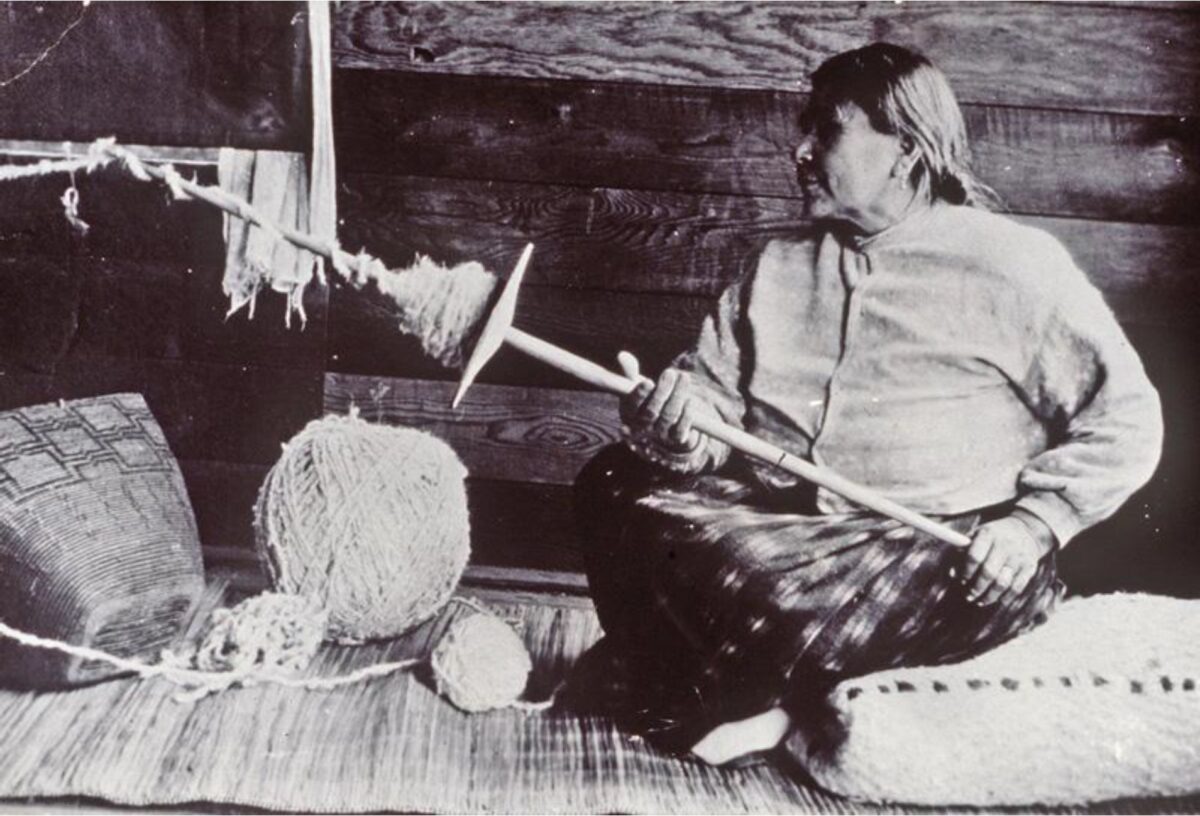
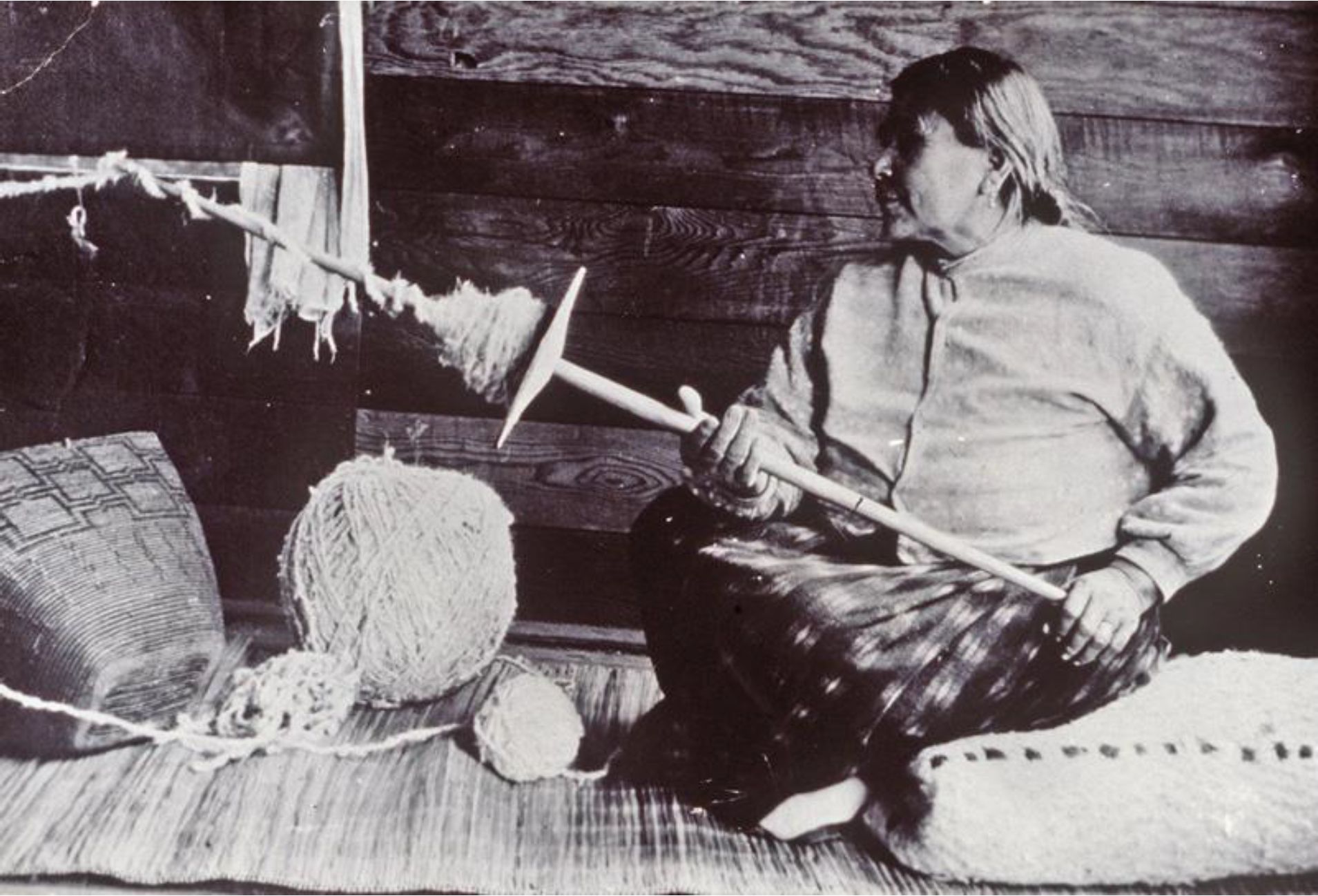
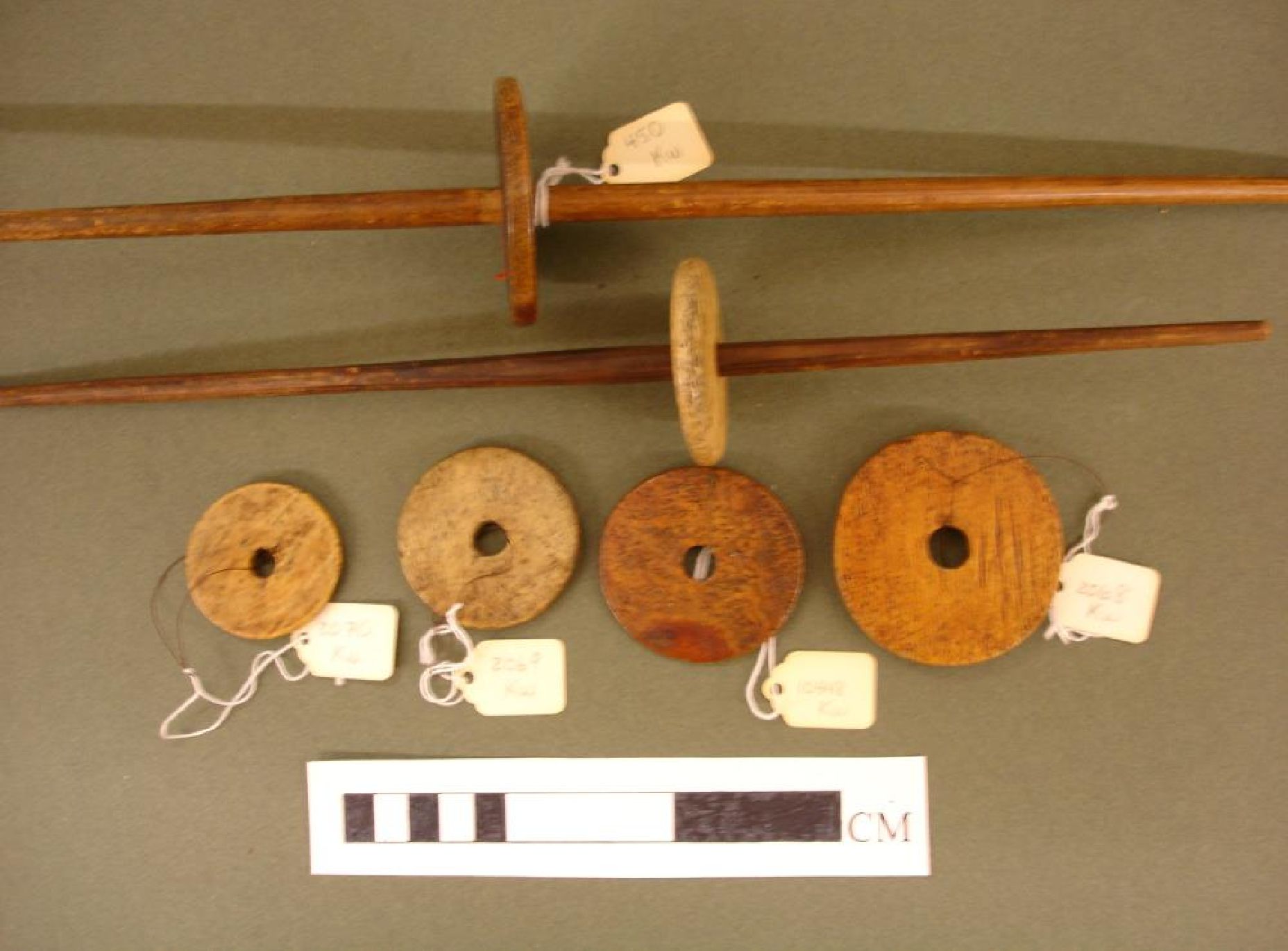
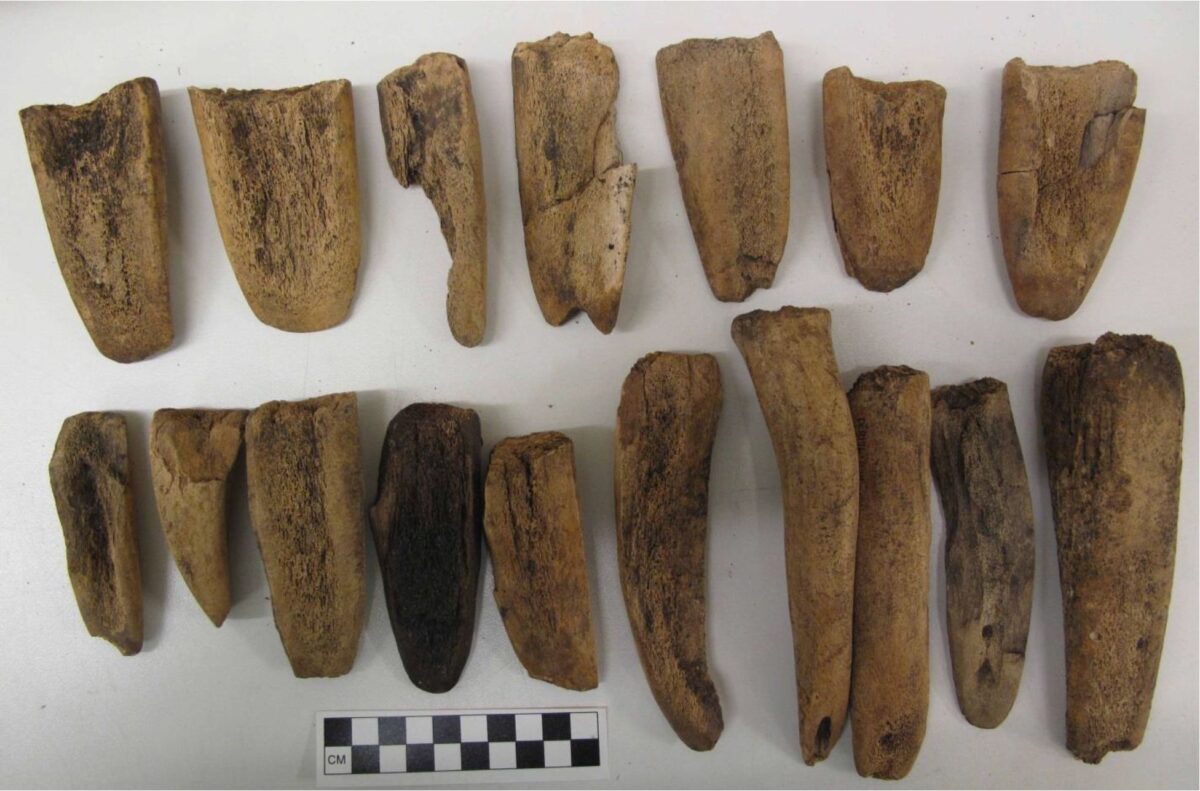
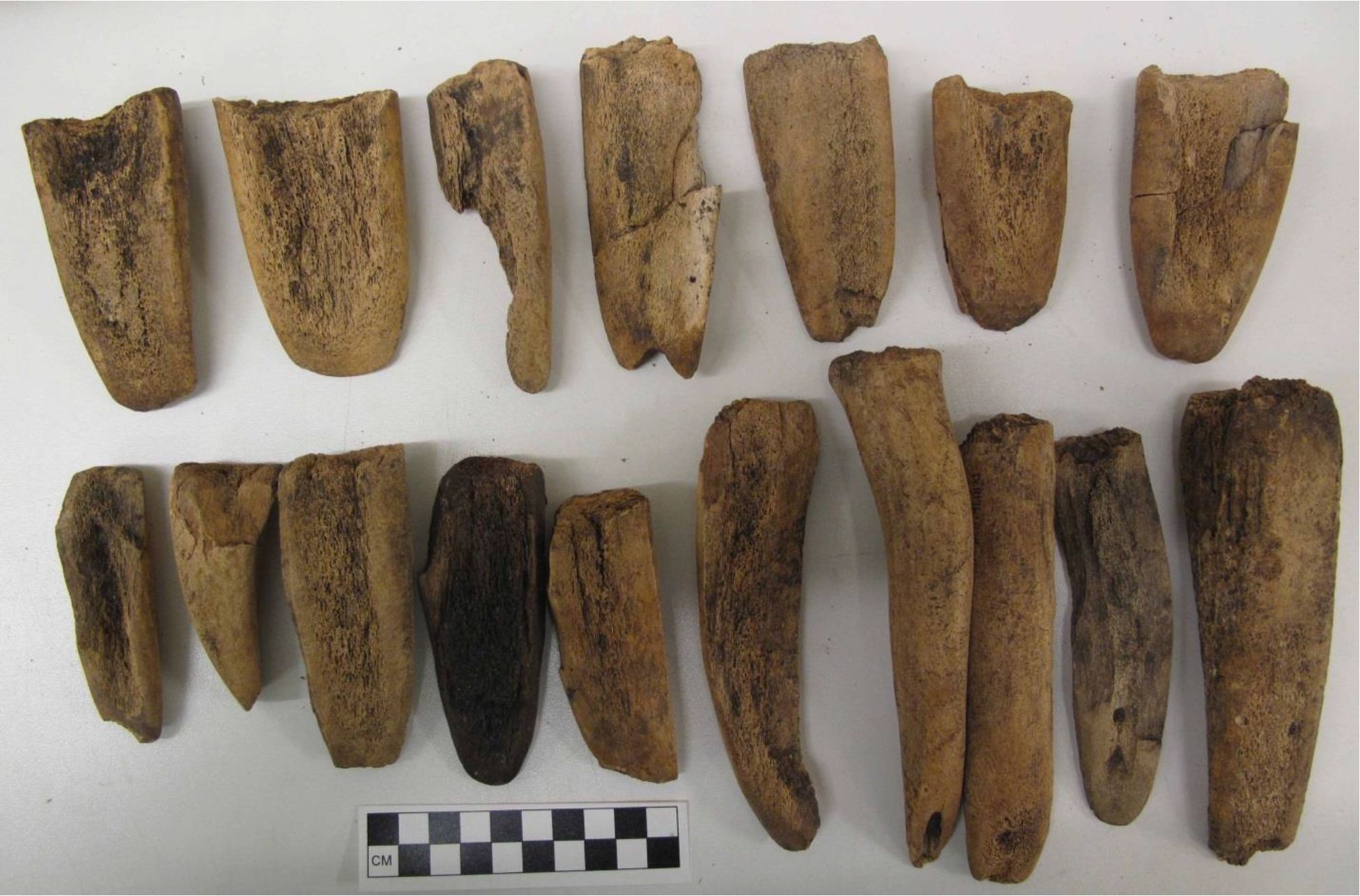
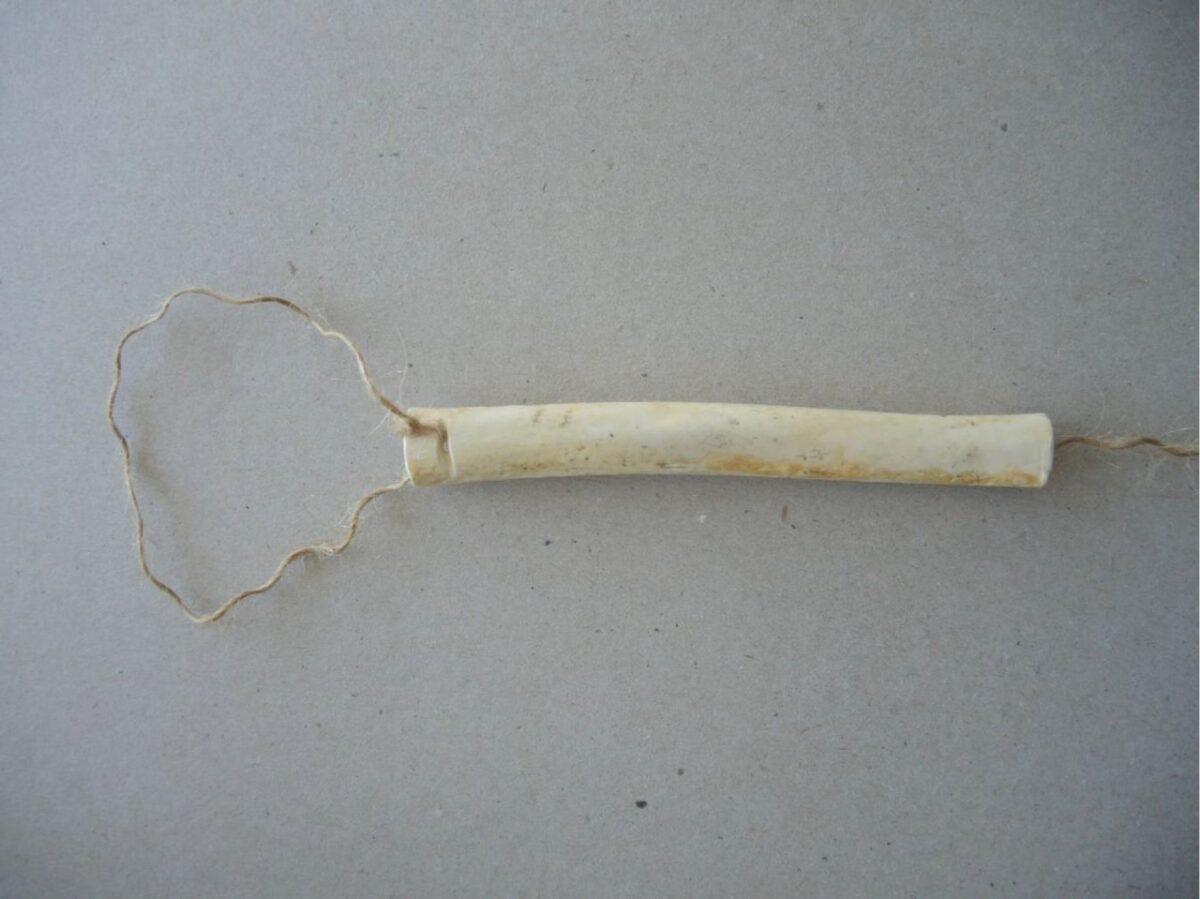
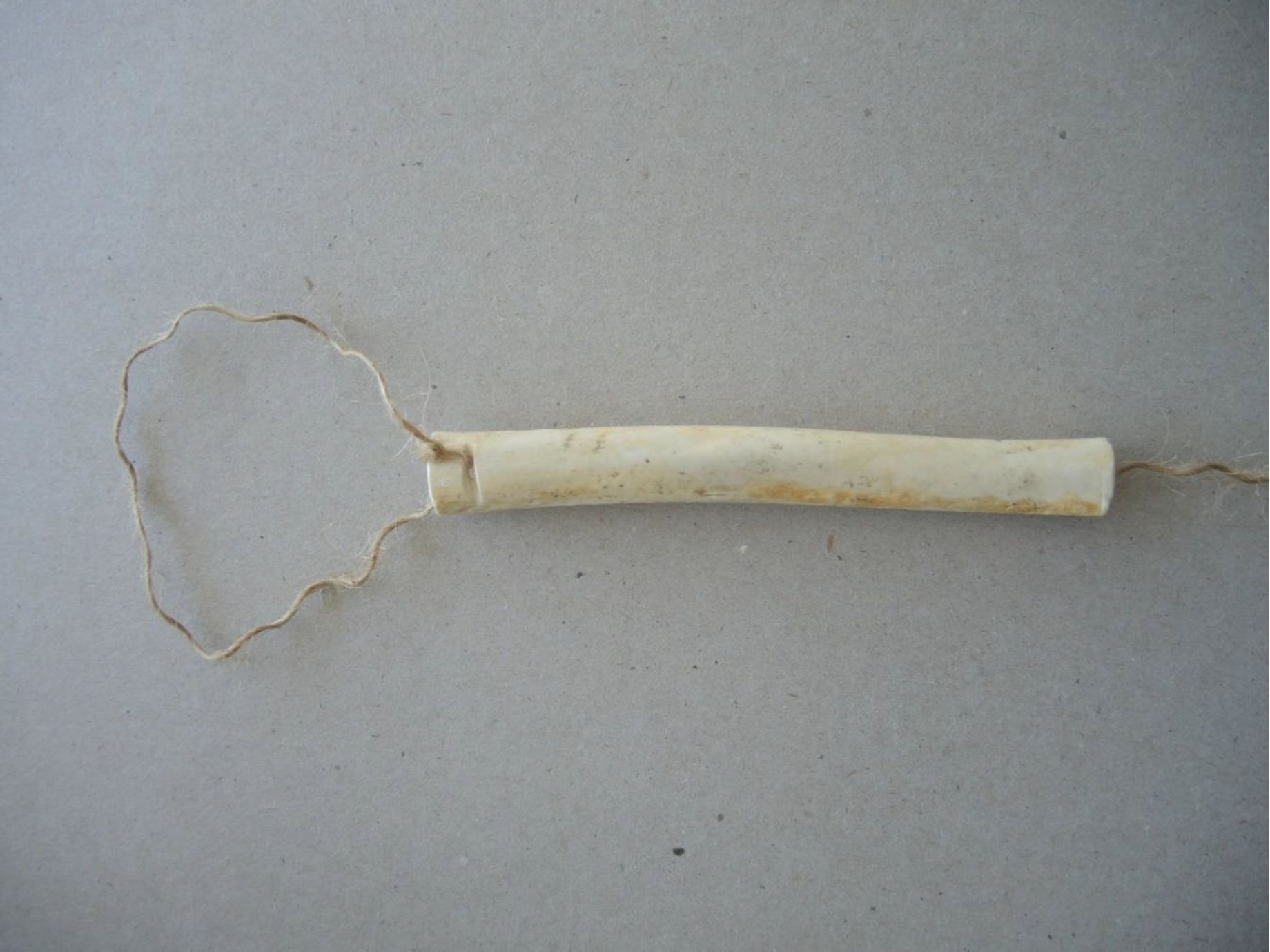
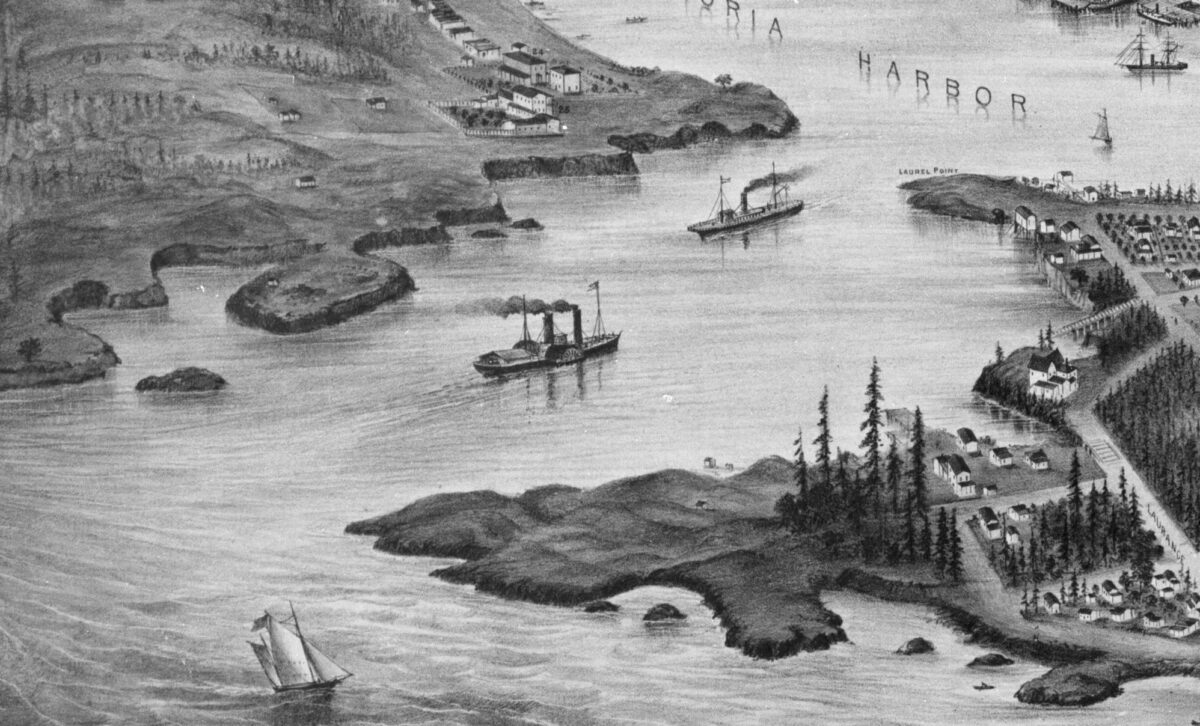
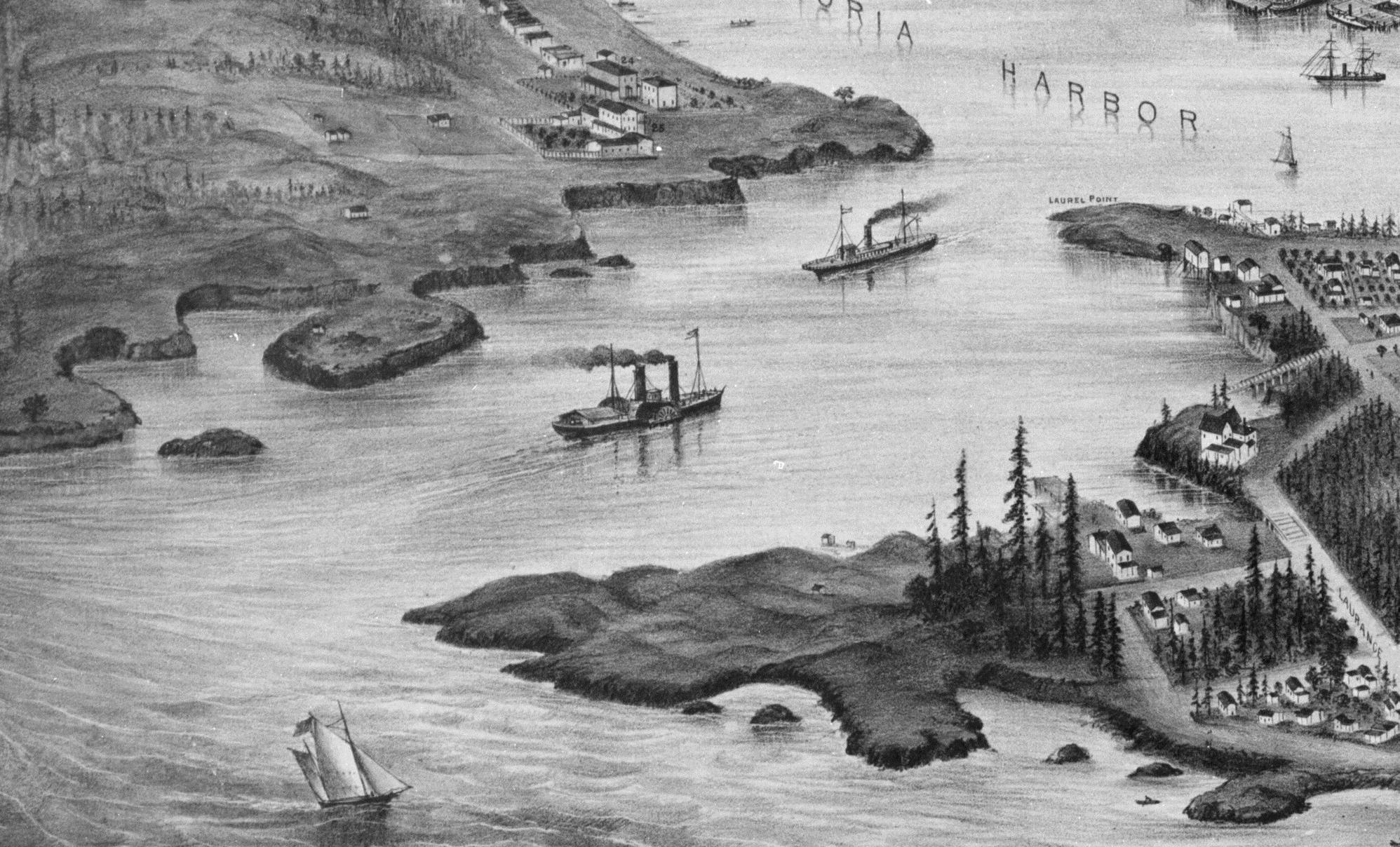
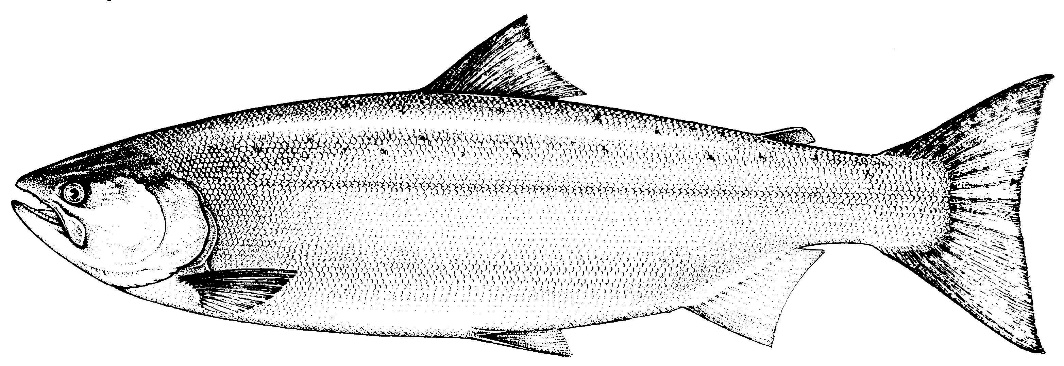
By Grant Keddie. Nov 2016. 19th century photographic images in the Victoria region that show Lekwungen (Esquimalt and Songhees First Nations) undertaking traditional food gathering practices are rare. The only example of fishing is a photograph, taken in 1868, by Frederick Dally in Esquimalt harbour at the south entrance to Lang Cove (RBCM PN905). Lang Cove is located south of Skinner’s Cove, both of which are within the larger Constance Cove. This is the location of an ancient shellmidden as demonstrated by the scattered white clam shells seen in the image and later observed by the author at this location. This image (fig. 1 and close-up fig.2) of a man and woman at a herring fishing site is listed in … Continue reading “A Lekwungen Herring Fishing site in Esquimalt Harbour: A Unique photograph in the Collection of the Royal B.C. Museum”